https://
%matplotlib widget
import sys
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.animation import FFMpegWriter, FuncAnimation
from tqdm.notebook import tqdm1 Introducción¶
Los métodos de volúmenes finitos son técnicas del análisis numérico el cual surgen de la discretización de una EDP en su forma conservativa.
2 Fundamentos básicos¶
2.1 Ley de conservación¶
Una ley de conservación unidimensional es
2.2 Sistemas lineales de leyes de conservación hiperbólicas¶
2.3 Problema de Cauchy¶
Si y , entonces .
2.4 Problema de Riemann¶
donde .
La solución es
2.5 Velocidad de propagación en algunos problemas evolutivos¶
2.5.1 Problemas parabólicos¶
2.5.2 Problemas hiperbólicos¶
3 Métodos de Volúmenes Finitos¶
Métodos descentrados de primer orden.
3.1 Método de Volúmenes Finitos¶
El método de volúmenes finitos es conservativo.
3.2 Métodos descentrados¶
3.2.1 Método descentrado upwind¶
Si ,
El flujo numérico a lo largo de la recta es
El flujo numérico a lo largo de la recta es
3.2.1 Método descentrado downwind¶
Si ,
, .
3.3 Método de Godunov¶
3.3.1 Primera versión¶
3.3.2 Segunda versión¶
4 Convergencia, precisión y estabilidad¶
Upwind
Downwind
FTCS
Lax-Friedrichs
Lax-Wendroff
4.2 Error de truncamiento local y consistencia¶
4.3 Estabilidad¶
4.3.1 Condición CFL¶
4.3.2 Análisis de Estabilidad de Von Neumann¶
5 Simulaciones numéricas¶
Introducimos las condiciones de contorno.
5.1 Condiciones de contorno¶
Extender el dominio computacional para incluir celdas en cada extremo, estas se llaman las celdas fantasmas.
Las condiciones de contorno periódicas,
Si , .
Si , .
5.2 Lenguaje de programación Julia¶
_
_ _ _(_)_ | Documentation: https://docs.julialang.org
(_) | (_) (_) |
_ _ _| |_ __ _ | Type "?" for help, "]?" for Pkg help.
| | | | | | |/ _` | |
| | |_| | | | (_| | | Version 1.11.2 (2024-12-01)
_/ |\__'_|_|_|\__'_| |
|__/ |
julia>5.3 Test numéricos¶
5.3.1 Primeros test¶
Ejemplo 1
, , , .
plt.style.use("seaborn-v0_8-white")def U(x):
return np.exp(-np.power(x - 15, 2))x = np.linspace(start=0, stop=20, num=300)
t, Δt = np.linspace(start=0, stop=1, num=51, retstep=True)
c = -1fig, ax = plt.subplots(layout="constrained")
ax.plot(
x,
U(x),
color="red",
label=r"$U_{0}\left(x\right)$",
linestyle="solid",
linewidth=1.0,
)
ax.spines["bottom"].set_color("none")
ax.spines["top"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["top"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["top"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.spines["left"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["left"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["left"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.spines["right"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["right"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["right"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.set_xlim(left=x[0], right=x[-1])
ax.set_ylim(bottom=0, top=1)
ax.set_title(
label=r"Condición inicial $U_{0}\left(x\right)=e^{-{\left(x-15\right)}^{2}}$",
loc="center",
)
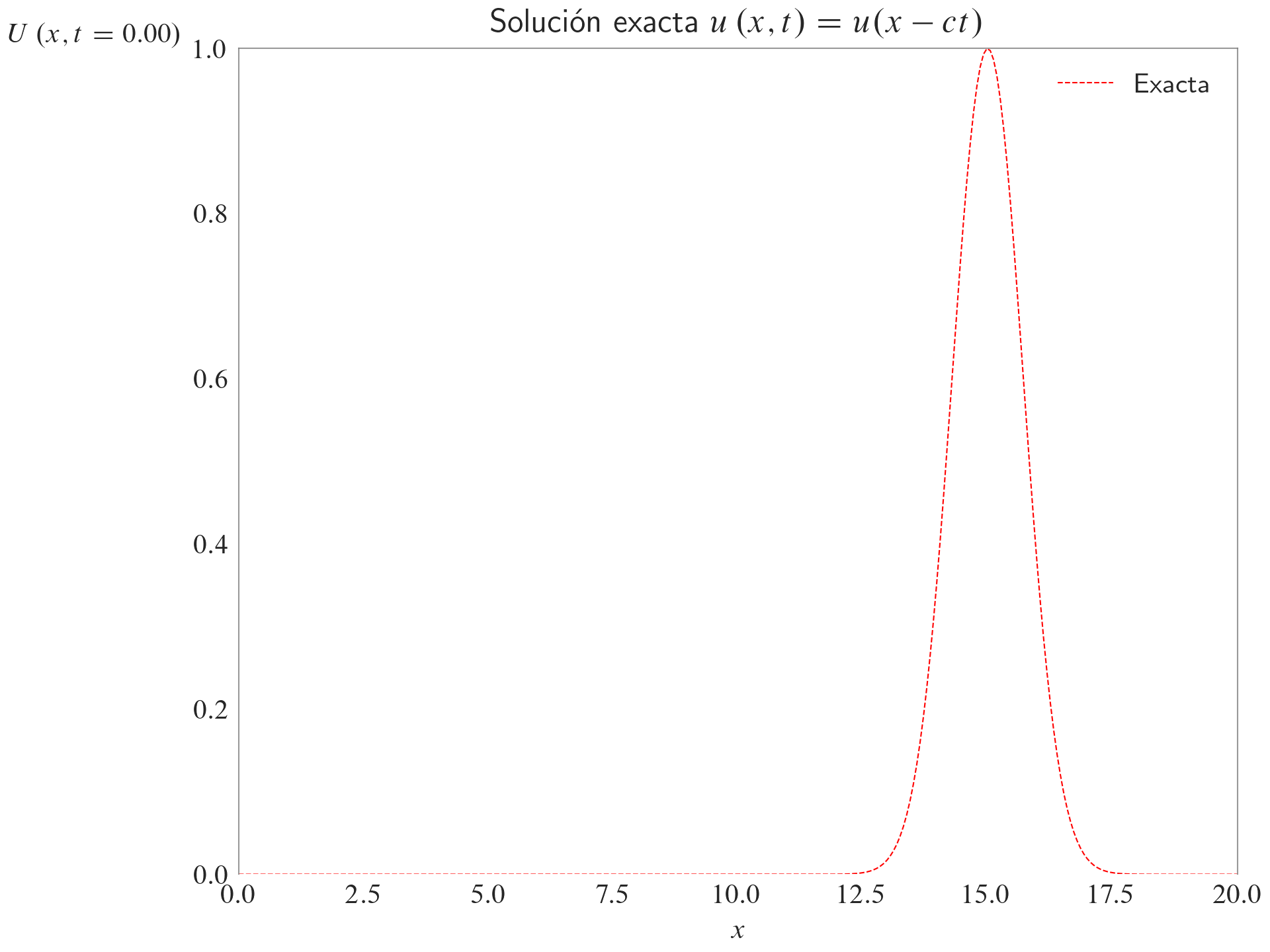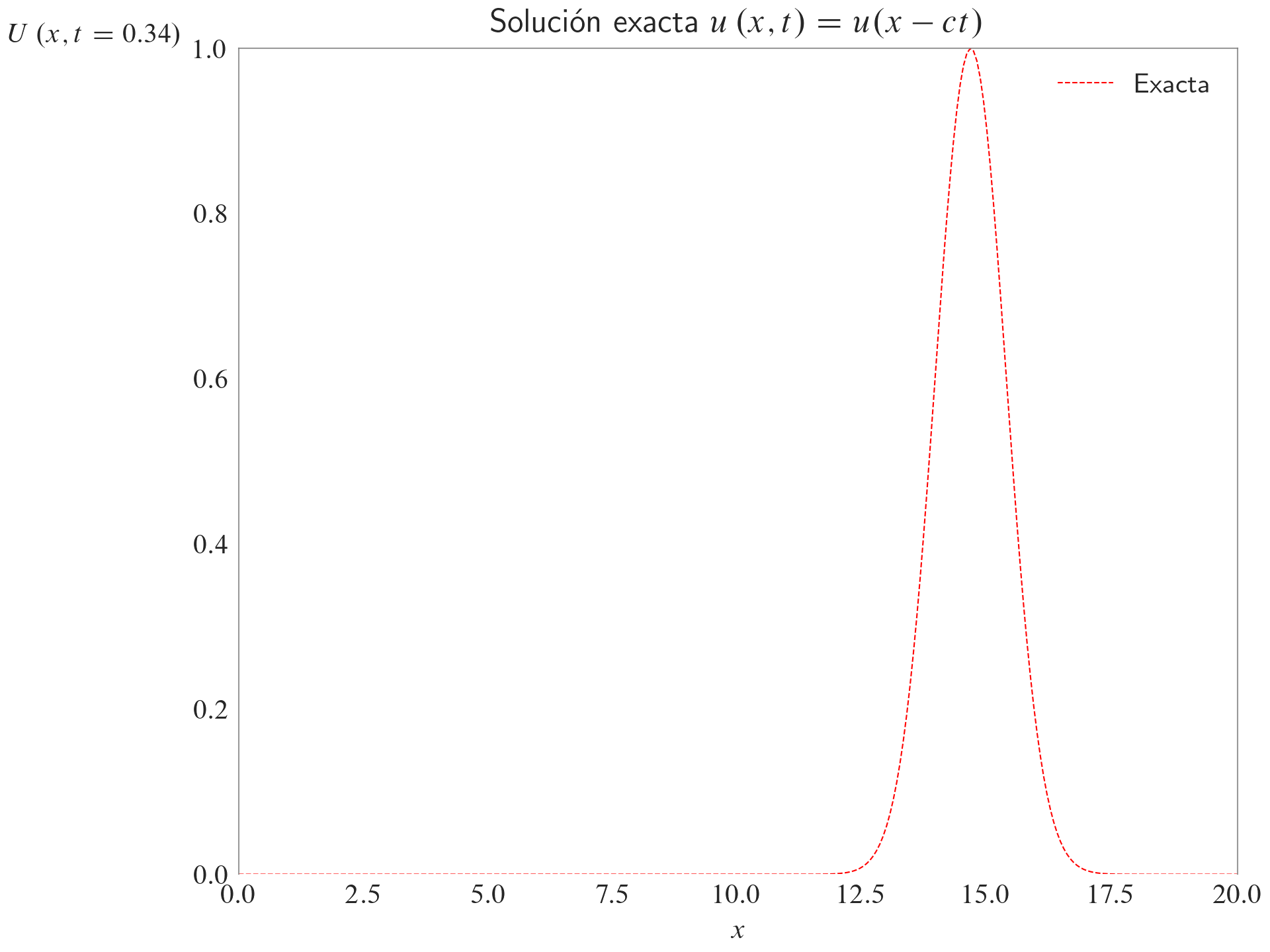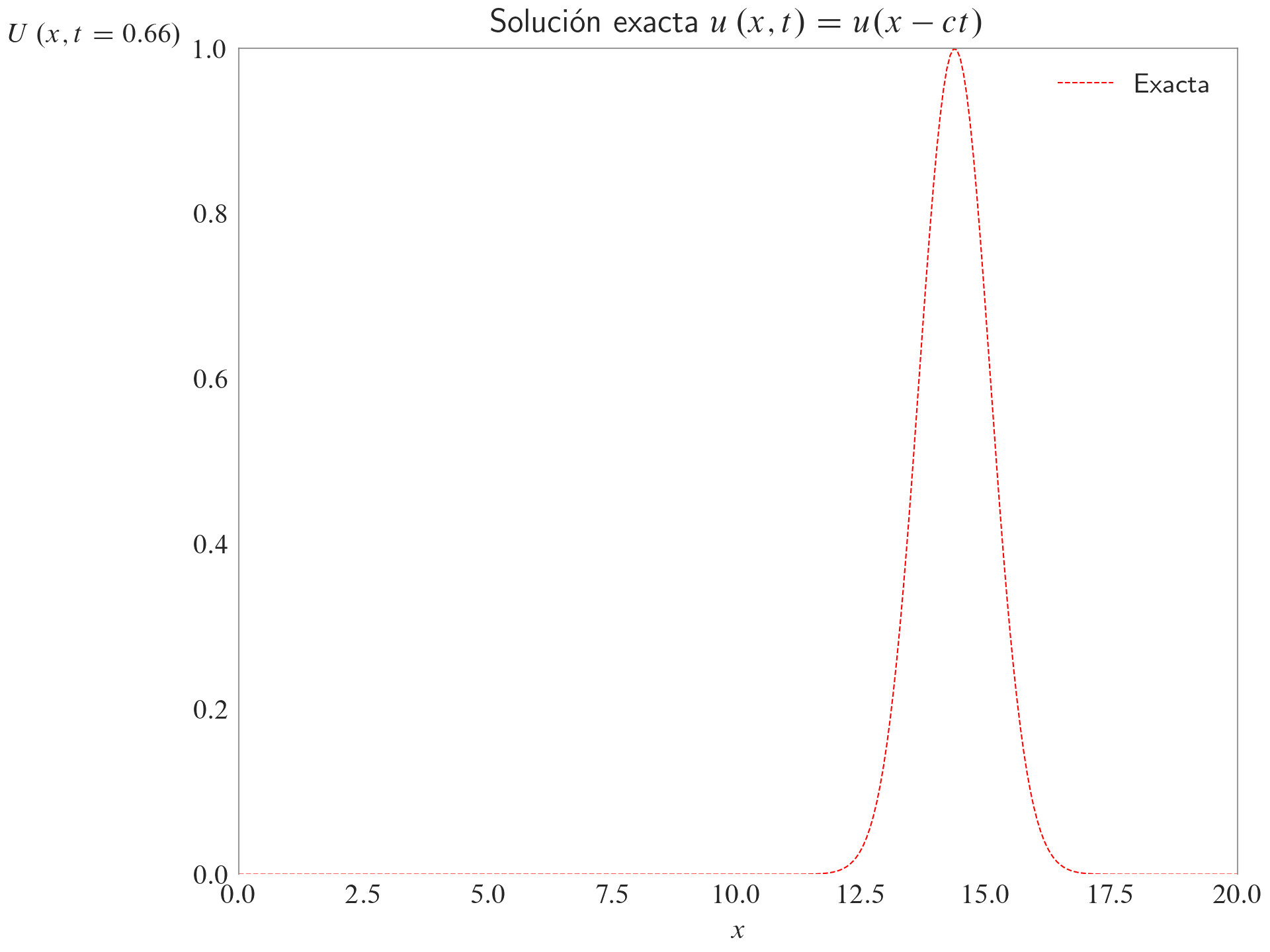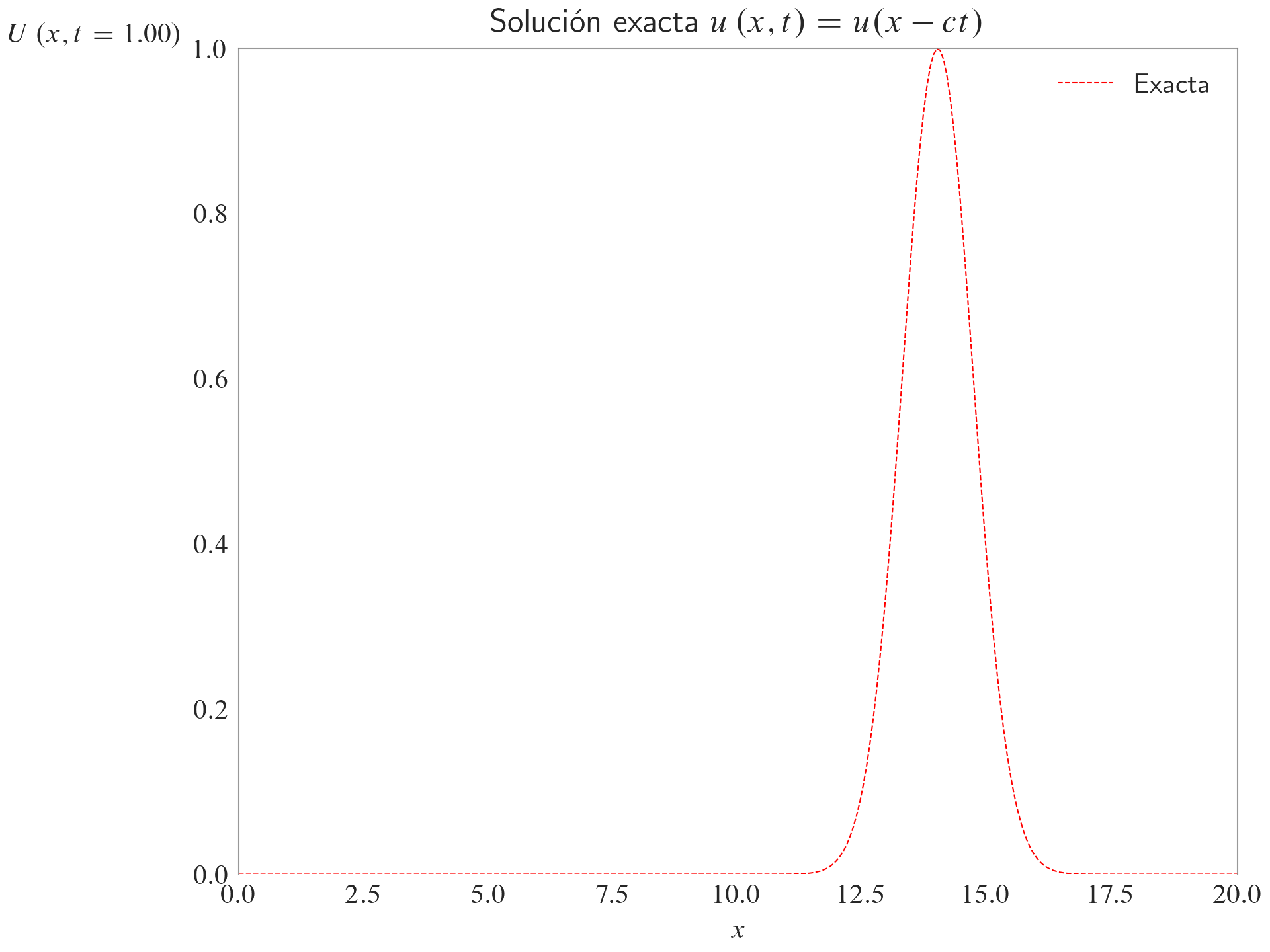
ax.legend(loc="best")Loading...
Solución exacta
fig, ax = plt.subplots(layout="constrained")
(ln,) = ax.plot(
[],
[],
color="red",
label="Exacta",
linestyle="dashed",
linewidth=0.5,
)
ax.spines["bottom"].set_color("none")
ax.spines["top"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["top"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["top"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.spines["left"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["left"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["left"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.spines["right"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["right"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["right"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.set_xlabel(xlabel=r"$x$")
ax.set_xlim(left=x[0], right=x[-1])
ax.set_ylim(bottom=0, top=1)
ax.set_title(label=r"Solución exacta $u\left(x,t\right)=u(x-ct)$")
ax.legend(loc="best")
def init():
ln.set_data(x, U(x))
return (ln,)
def update(frame):
ln.set_data(x, U(x=x - c * (t[0] + frame * Δt)))
ax.set_ylabel(
ylabel=rf"$U\left(x, t={frame * Δt:.2f}\right)$", loc="top", rotation=0
)
return (ln,)
anim = FuncAnimation(
fig=fig,
func=update,
frames=tqdm(iterable=range(t.size), file=sys.stdout, colour="green"),
interval=1,
init_func=init,
blit=True,
).save(
filename="exactgaussian.gif",
writer=FFMpegWriter(
fps=90,
codec="libx265",
metadata={
"subject": "Numerical Analysis",
"title": "Exact solution Gaussian Function",
"author": "Gloria Almozara Sainz",
"genre": "Mathematics",
"copyright": "2025",
"srcform": "Matplotlib 3.9.3",
"comment": "Numerical Simulation for advection PDE",
},
),
dpi=300,
savefig_kwargs={"transparent": True, "facecolor": "none"},
)
plt.close()Loading...
x, Δx = np.linspace(start=0, stop=20, num=201, retstep=True)
c = -1
cfl = c * Δt / Δxfig, ax = plt.subplots(layout="constrained")
(ln,) = ax.plot(
[],
[],
color="DarkBlue",
label="Exacta",
linestyle="dashed",
linewidth=0.5,
)
ln1 = ax.scatter(
x=[],
y=[],
c="blue",
label=rf"CFL $={cfl:.1f}$, $\Delta x={Δx:.3f}$",
s=0.4,
)
ax.set_xlabel(xlabel=r"$x$")
ax.set_xlim(left=x[0], right=x[-1])
ax.set_ylim(bottom=0, top=1)
ax.spines["bottom"].set_color("none")
ax.spines["top"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["top"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["top"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.spines["left"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["left"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["left"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.spines["right"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["right"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["right"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.set_title(label="Método Downwind para la función gaussiana", loc="center")
ax.legend(loc="best")
U1 = U(x=x)
def init():
ln.set_data(x, U(x))
ln1.set_offsets(offsets=np.column_stack([x, U1]))
return (ln,)
def update(frame):
ln1.set_offsets(offsets=np.column_stack([x, U1]))
ln.set_data(x, U(x=x - c * frame * Δt))
U1[1:] -= cfl * (np.roll(U1, -1) - U1)[1:]
ax.set_ylabel(
ylabel=rf"$U\left(x, t={frame * Δt:.2f}\right)$", loc="top", rotation=0
)
return (ln,)
anim = FuncAnimation(
fig=fig,
func=update,
frames=tqdm(iterable=range(t.size), file=sys.stdout, colour="green"),
interval=1,
init_func=init,
blit=True,
).save(
filename="downwindgaussian.gif",
writer=FFMpegWriter(
fps=90,
codec="libx265",
metadata={
"subject": "Numerical Analysis",
"title": "Exact solution",
"author": "Gloria Almozara Sainz",
"genre": "Mathematics",
"copyright": "2025",
"srcform": "Matplotlib 3.9.3",
"comment": "Numerical Simulation for advection PDE",
},
),
dpi=300,
savefig_kwargs={"transparent": True, "facecolor": "none"},
)
plt.close()Loading...
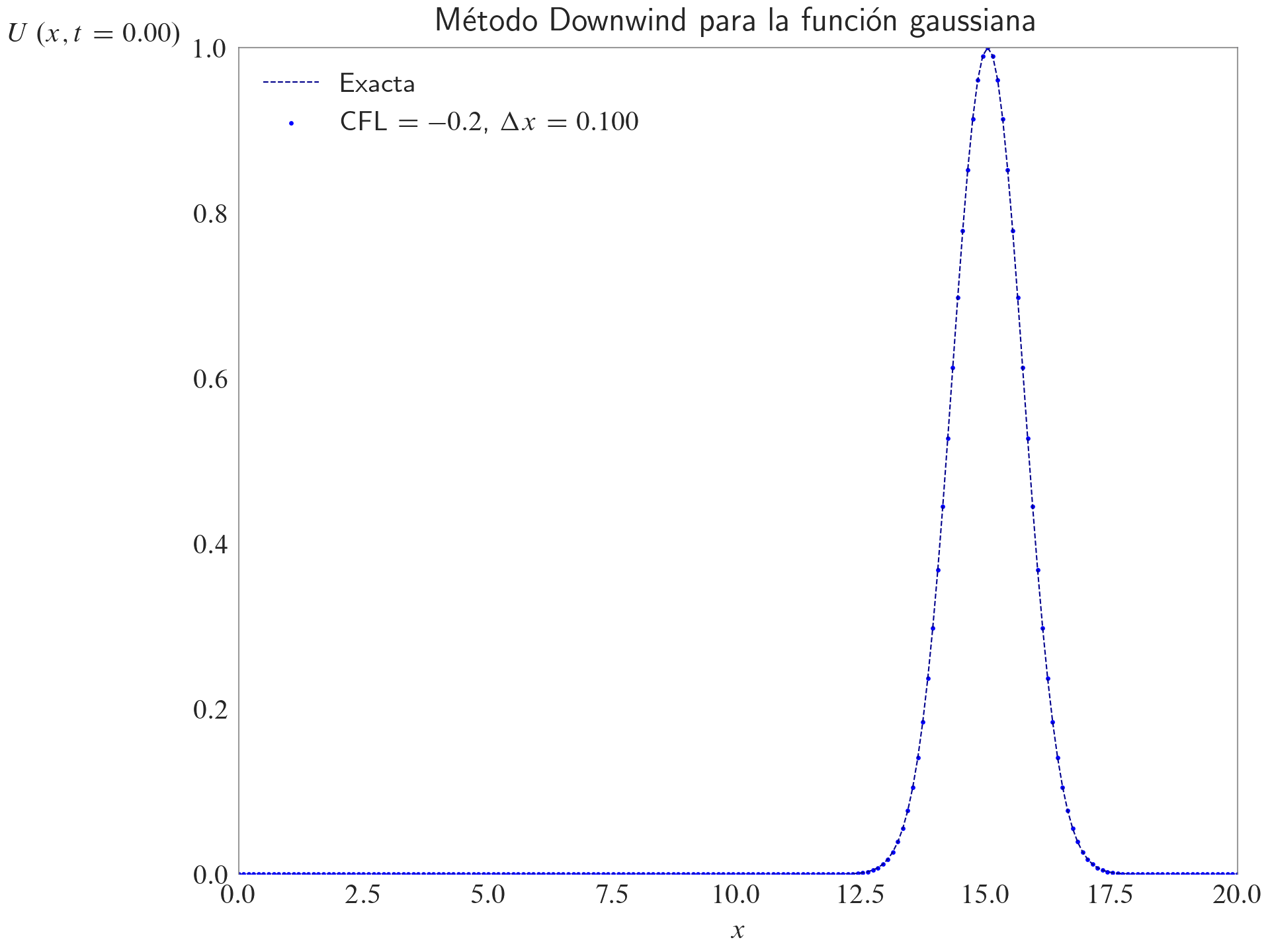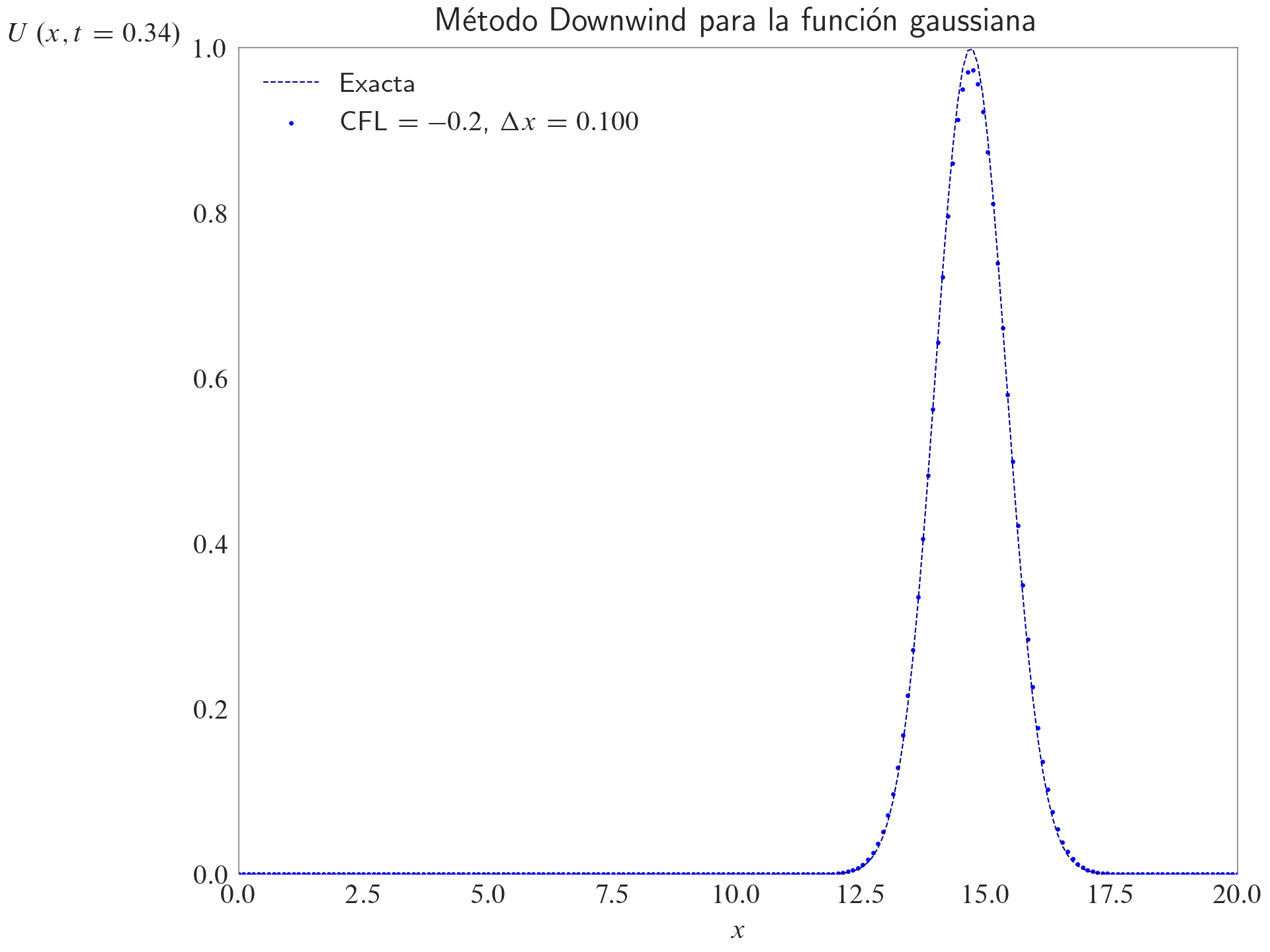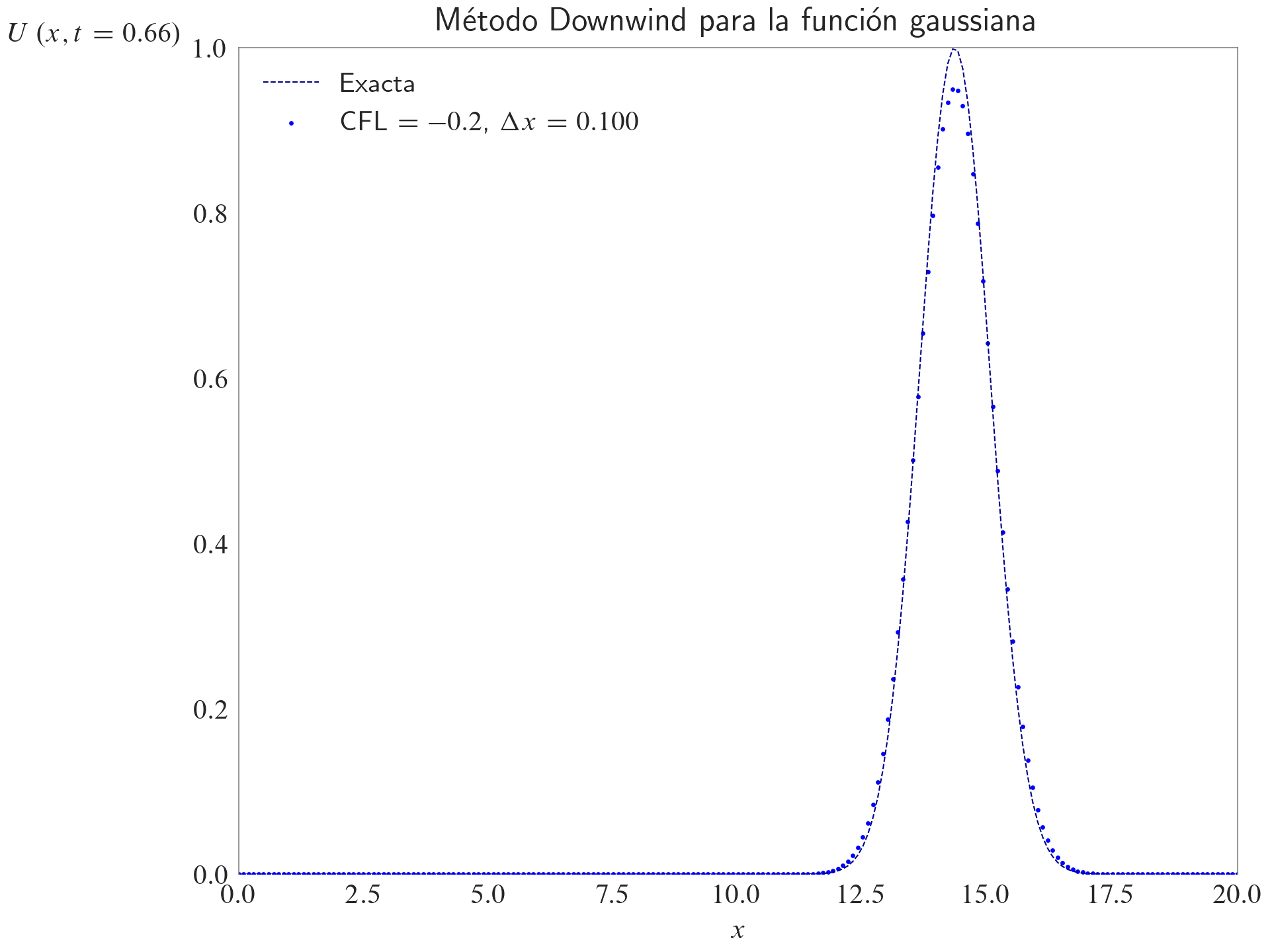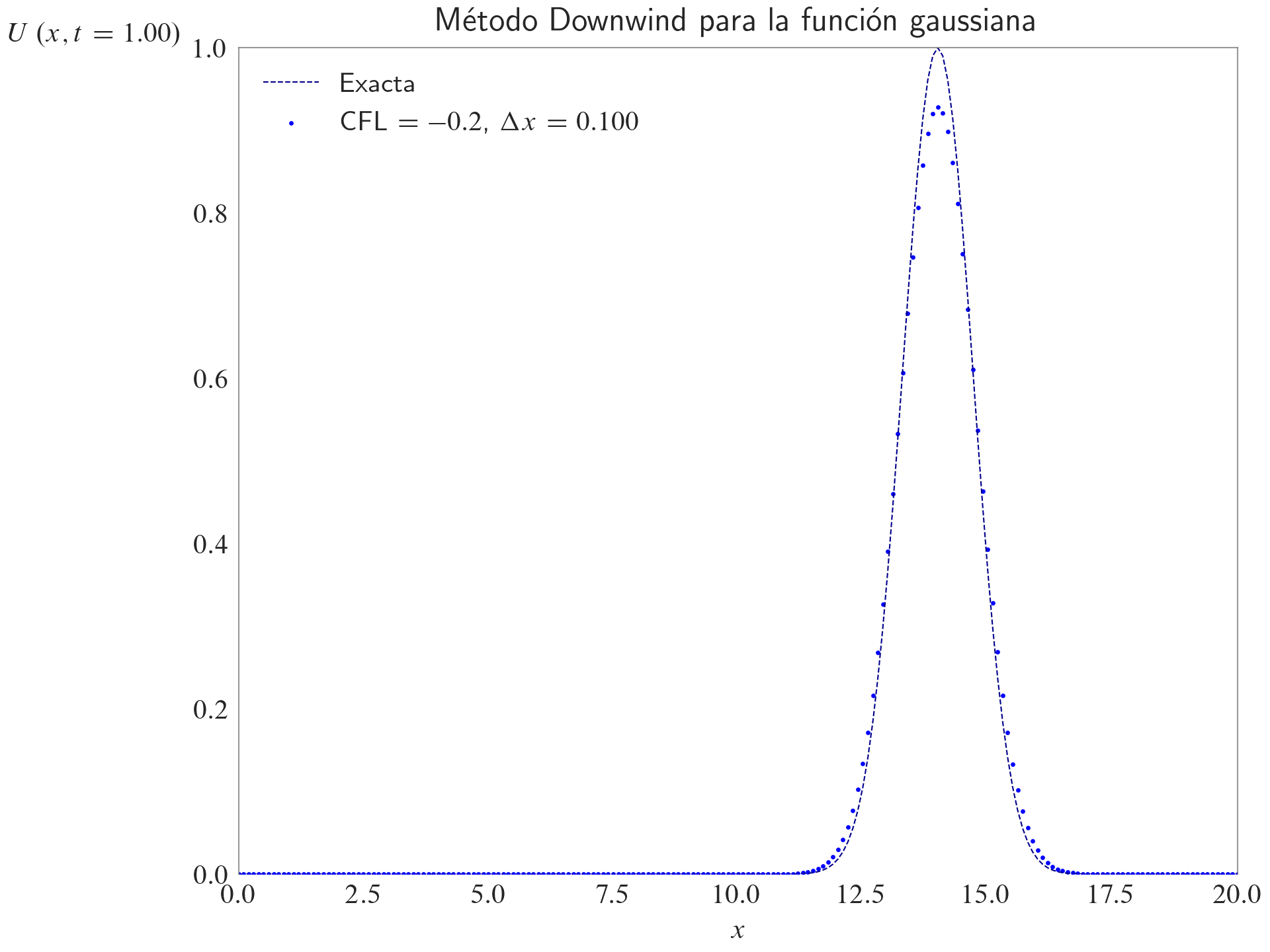
fig, ax = plt.subplots(layout="constrained")
(ln,) = ax.plot(
[],
[],
color="DarkBlue",
label="Exacta",
linestyle="dashed",
linewidth=0.5,
)
ln1 = ax.scatter(
x=[],
y=[],
c="blue",
label=rf"CFL $={cfl:.1f}$, $\Delta x={Δx:.3f}$",
s=0.4,
)
ax.set_xlabel(xlabel=r"$x$")
ax.set_xlim(left=x[0], right=x[-1])
ax.set_ylim(bottom=0, top=1)
ax.spines["bottom"].set_color("none")
ax.spines["top"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["top"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["top"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.spines["left"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["left"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["left"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.spines["right"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["right"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["right"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
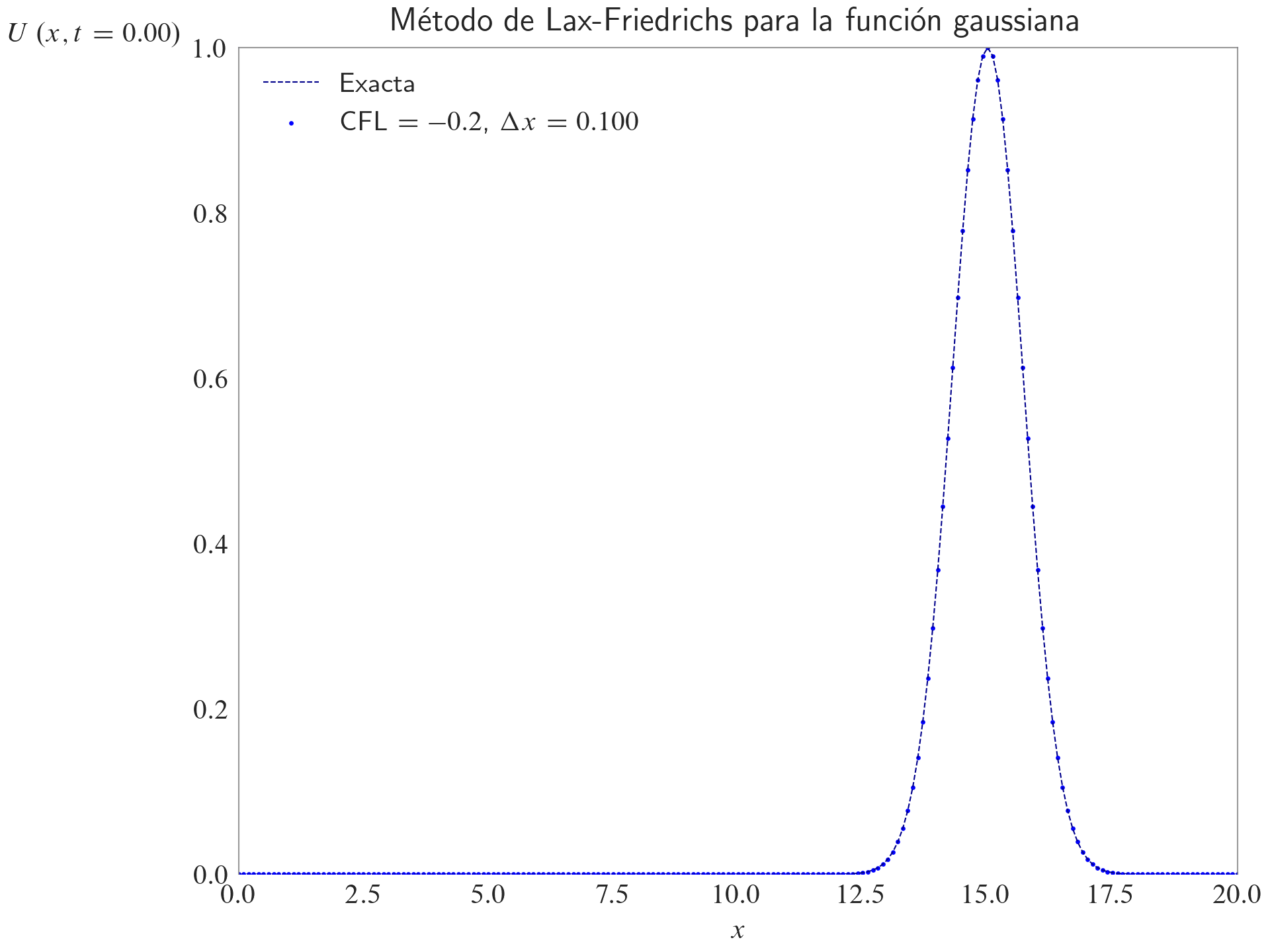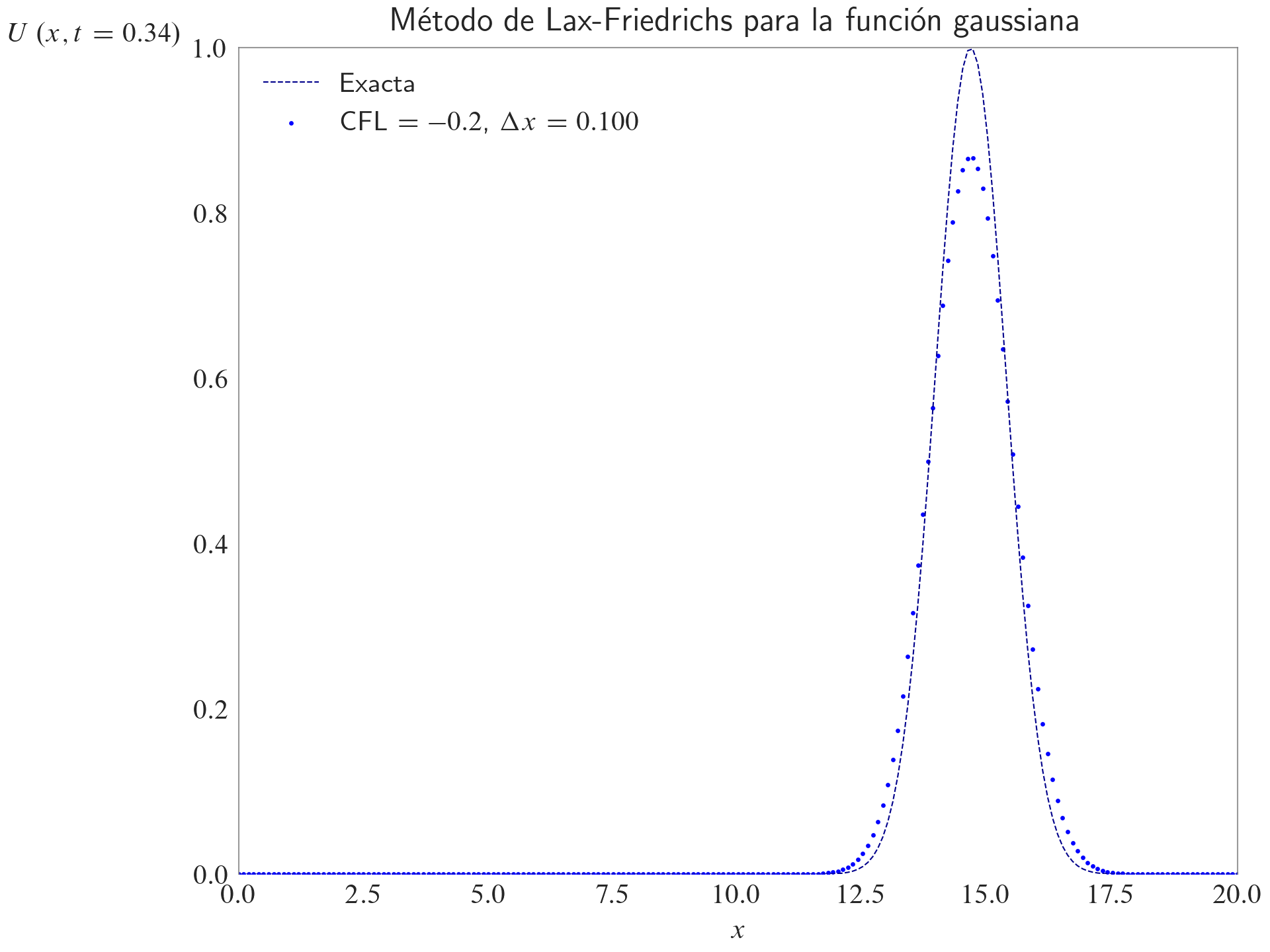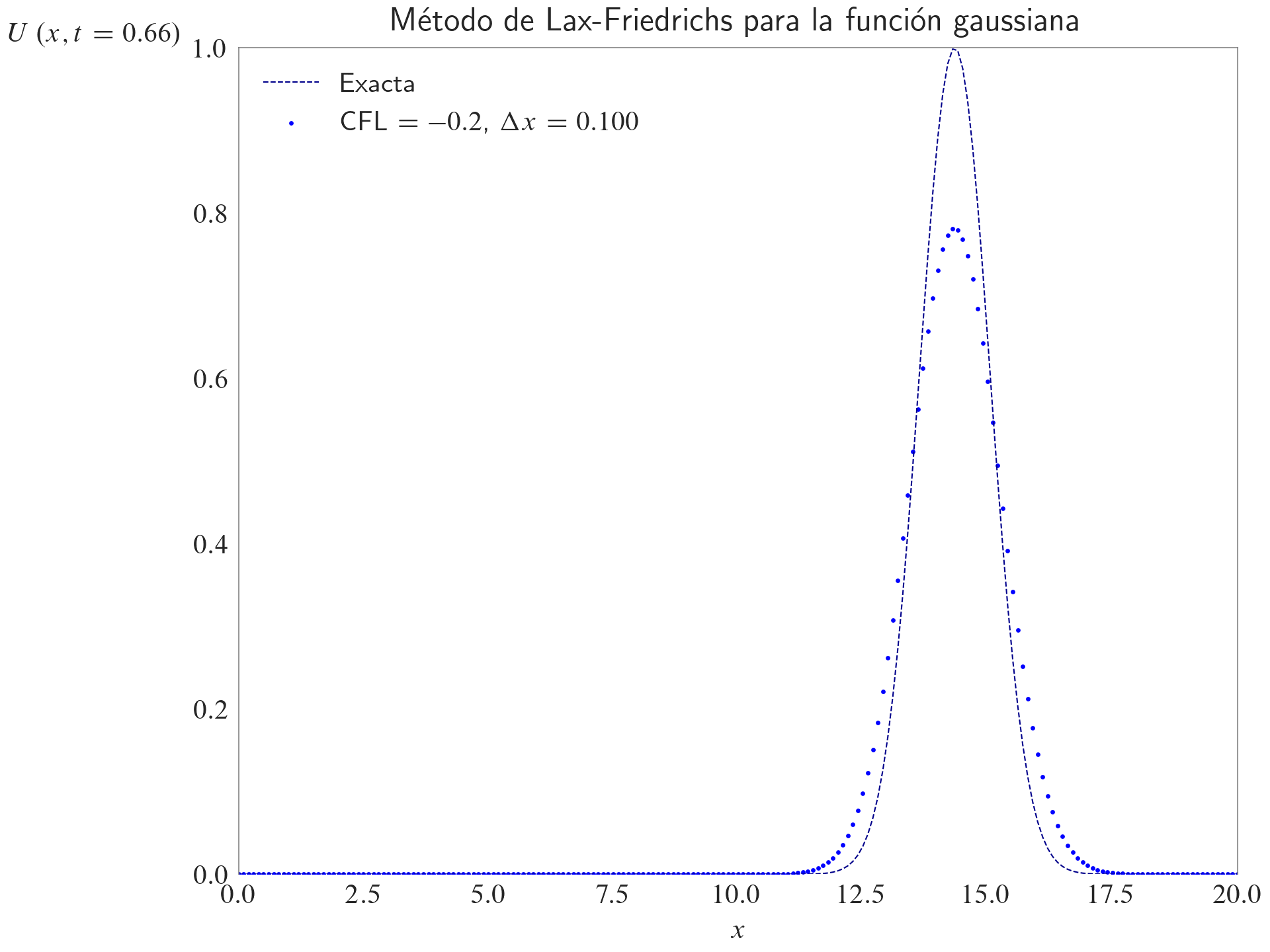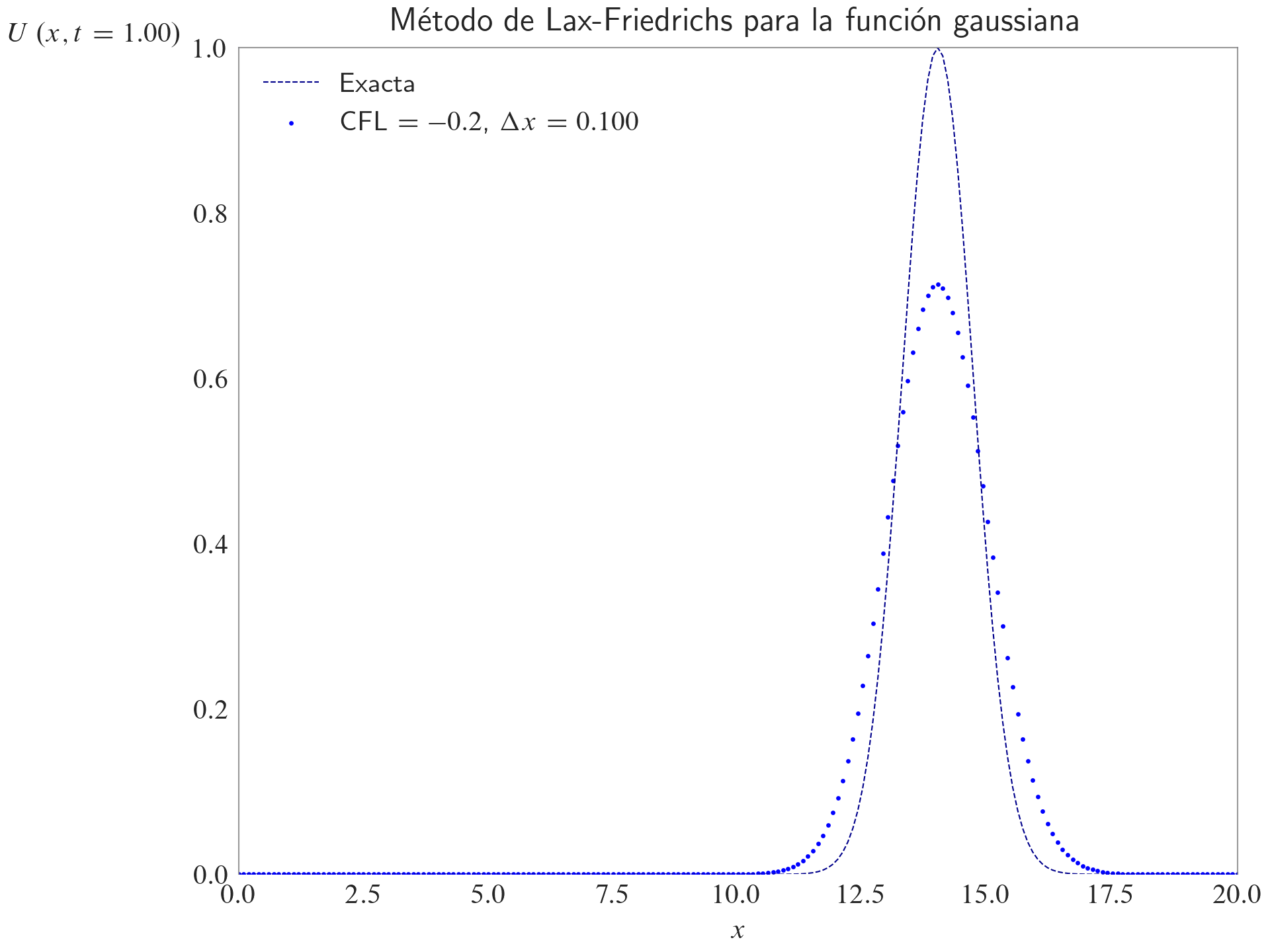
ax.set_title(label="Método de Lax-Friedrichs para la función gaussiana", loc="center")
ax.legend(loc="best")
U1 = U(x=x)
def init():
ln.set_data(x, U(x))
ln1.set_offsets(offsets=np.column_stack([x, U1]))
return (ln,)
def update(frame):
ln1.set_offsets(offsets=np.column_stack([x, U1]))
ln.set_data(x, U(x=x - c * frame * Δt))
U1[1:-1] = (
0.5 * (np.roll(U1, -1) + np.roll(U1, 1))[1:-1]
- 0.5 * cfl * (np.roll(U1, -1) - np.roll(U1, 1))[1:-1]
)
ax.set_ylabel(
ylabel=rf"$U\left(x, t={frame * Δt:.2f}\right)$", loc="top", rotation=0
)
return (ln,)
anim = FuncAnimation(
fig=fig,
func=update,
frames=tqdm(iterable=range(t.size), file=sys.stdout, colour="green"),
interval=1,
init_func=init,
blit=True,
).save(
filename="lax-friedrichsgaussiana.gif",
writer=FFMpegWriter(
fps=90,
codec="libx265",
metadata={
"subject": "Numerical Analysis",
"title": "Exact solution",
"author": "Gloria Almozara Sainz",
"genre": "Mathematics",
"copyright": "2025",
"srcform": "Matplotlib 3.9.3",
"comment": "Numerical Simulation for advection PDE",
},
),
dpi=300,
savefig_kwargs={"transparent": True, "facecolor": "none"},
)
plt.close()Loading...
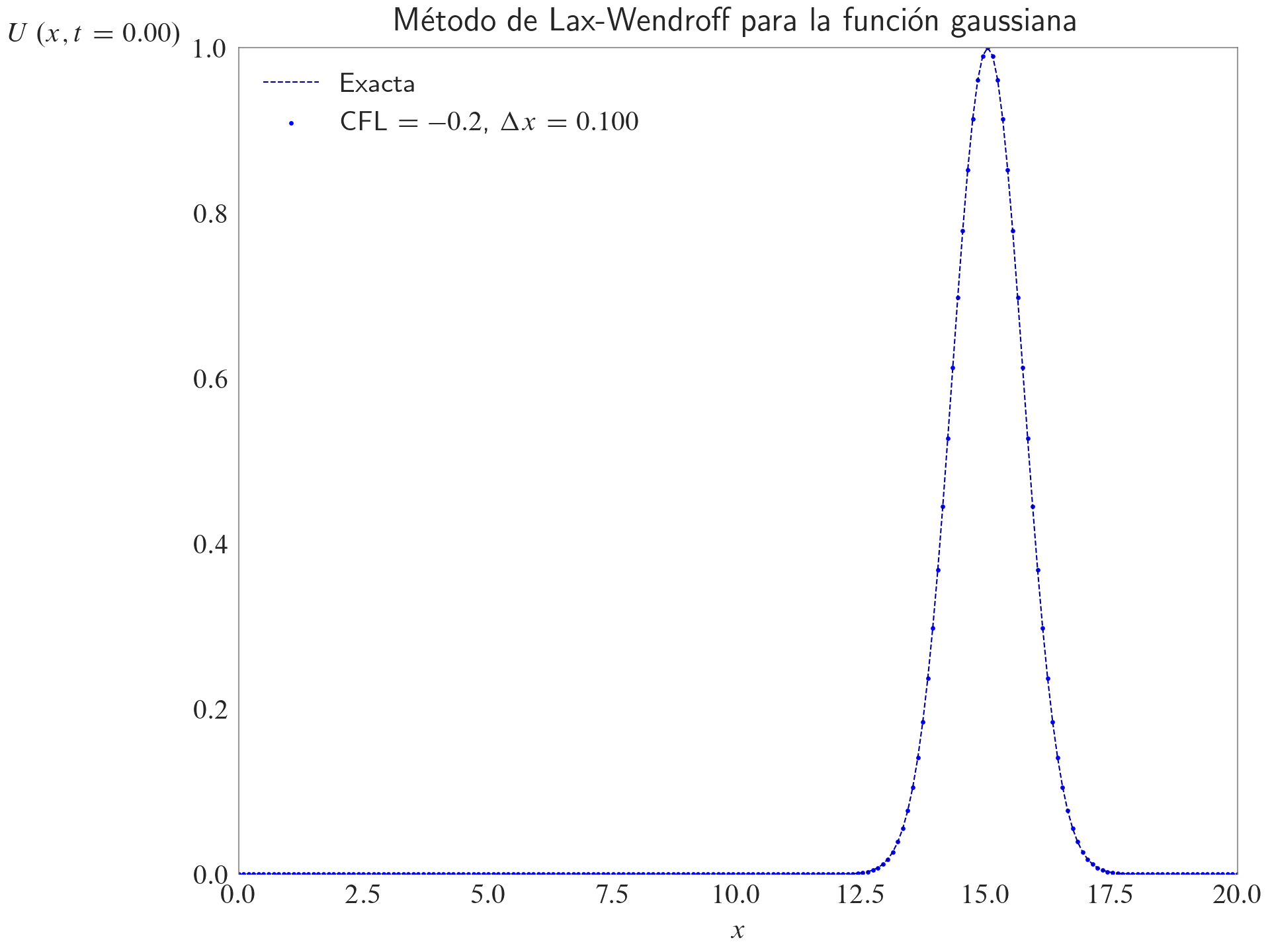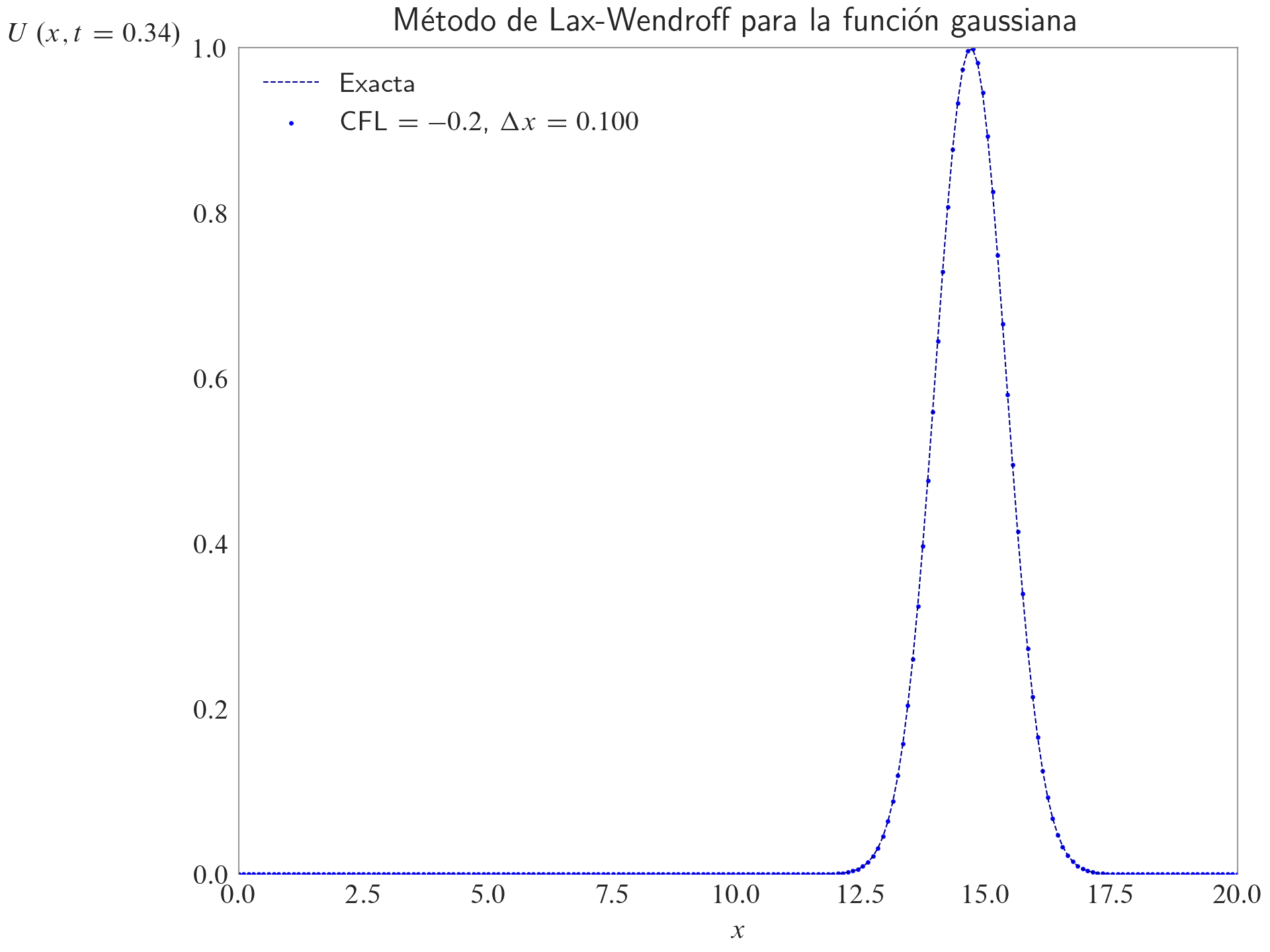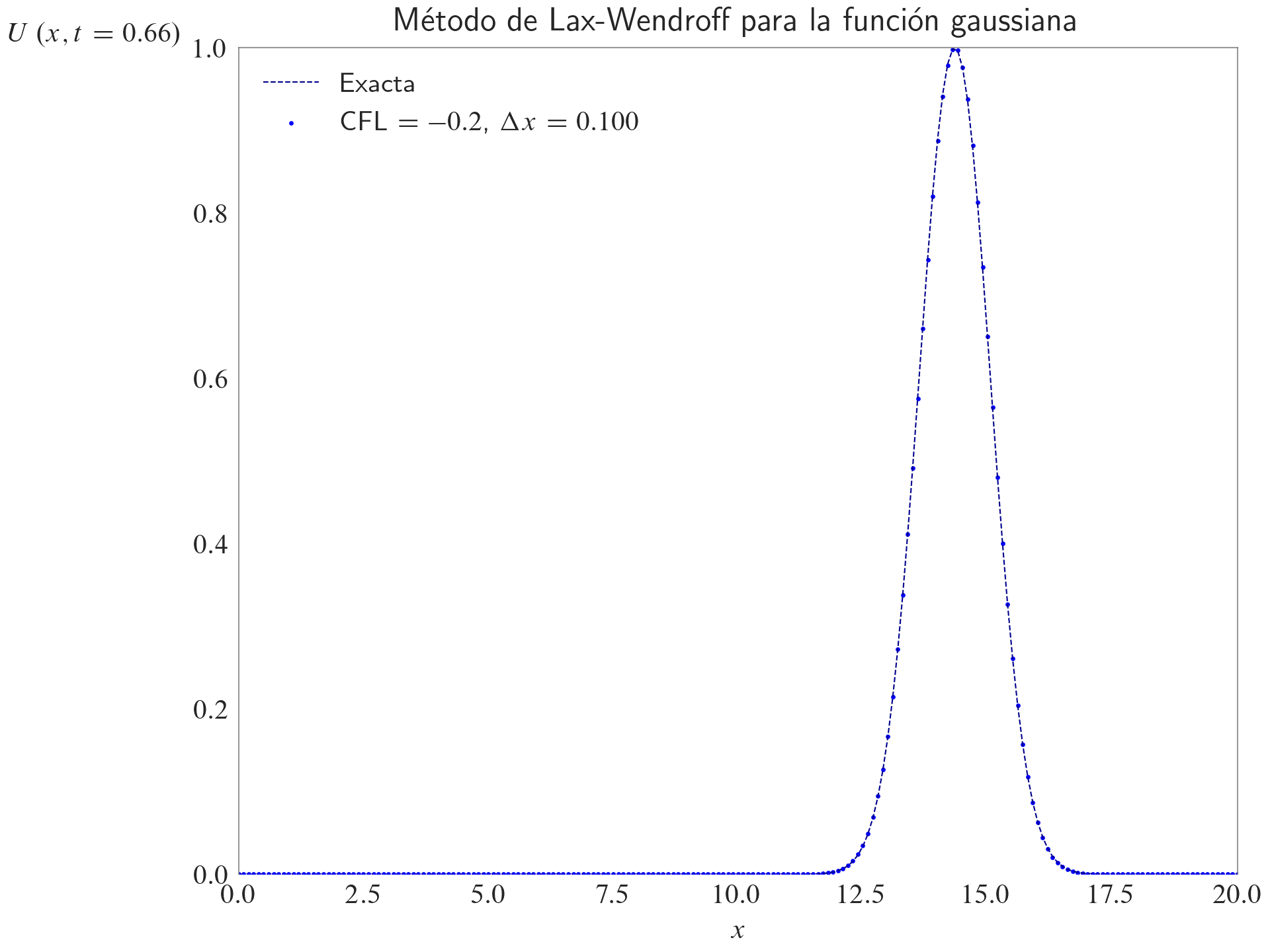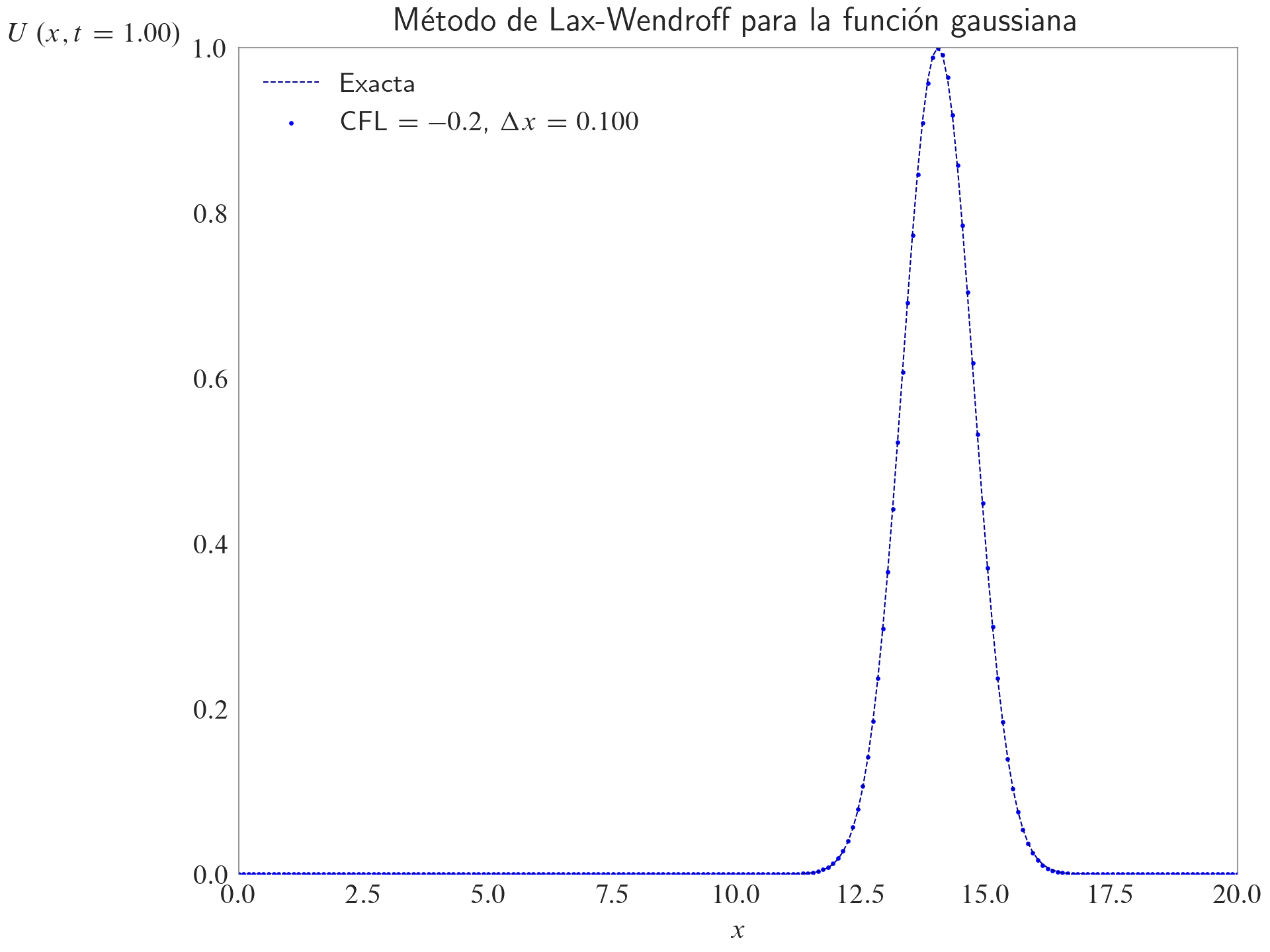
Método de Lax-Wendroff
fig, ax = plt.subplots(layout="constrained")
(ln,) = ax.plot(
[],
[],
color="DarkBlue",
label="Exacta",
linestyle="dashed",
linewidth=0.5,
)
ln1 = ax.scatter(
x=[],
y=[],
c="blue",
label=rf"CFL $={cfl:.1f}$, $\Delta x={Δx:.3f}$",
s=0.4,
)
ax.spines["bottom"].set_color("none")
ax.spines["top"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["top"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["top"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.spines["left"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["left"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["left"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.spines["right"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["right"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["right"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.set_xlabel(xlabel=r"$x$")
ax.set_xlim(left=x[0], right=x[-1])
ax.set_ylim(bottom=0, top=1)
ax.set_title(label="Método de Lax-Wendroff para la función gaussiana", loc="center")
ax.legend(loc="best")
U1 = U(x=x)
def init():
ln.set_data(x, U(x))
ln1.set_offsets(offsets=np.column_stack([x, U1]))
return (ln,)
def update(frame):
ln1.set_offsets(offsets=np.column_stack([x, U1]))
ln.set_data(x, U(x=x - c * frame * Δt))
U1[1:-1] -= (
0.5 * cfl * (np.roll(U1, -1) - np.roll(U1, 1))[1:-1]
- 0.5 * cfl**2 * (np.roll(U1, -1) - 2 * U1 + np.roll(U1, 1))[1:-1]
)
ax.set_ylabel(
ylabel=rf"$U\left(x, t={frame * Δt:.2f}\right)$", loc="top", rotation=0
)
return (ln,)
anim = FuncAnimation(
fig=fig,
func=update,
frames=tqdm(iterable=range(t.size), file=sys.stdout, colour="green"),
interval=1,
init_func=init,
blit=True,
).save(
filename="lax-wendroffgaussiana.gif",
writer=FFMpegWriter(
fps=90,
codec="libx265",
metadata={
"subject": "Numerical Analysis",
"title": "Exact solution",
"author": "Gloria Almozara Sainz",
"genre": "Mathematics",
"copyright": "2025",
"srcform": "Matplotlib 3.9.3",
"comment": "Numerical Simulation for advection PDE",
},
),
dpi=300,
savefig_kwargs={"transparent": True, "facecolor": "none"},
)
plt.close()Loading...
x, Δx = np.linspace(start=0, stop=30, num=251, retstep=True)
t, Δt = np.linspace(start=0, stop=1, num=51, retstep=True)
c = 1
cfl = c * Δt / Δxdef U(x, U_left=2, U_right=1, x0=15):
return U_left + (U_right - U_left) * np.heaviside(x - x0, 0)fig, ax = plt.subplots(layout="constrained")
ax.plot(
x,
U(x),
color="red",
label=r"$U_{0}\left(x\right)$",
linestyle="solid",
linewidth=1.0,
)
ax.spines["bottom"].set_color("none")
ax.spines["top"].set_color("none")
ax.spines["left"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["left"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["left"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.spines["right"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["right"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["right"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.set_title(label=r"Condición inicial $U_{0}=2-H\left(x-15\right)$", loc="center")
ax.set_xlim(left=x[0], right=x[-1])
ax.set_ylim(bottom=U(x).min(), top=U(x).max())
ax.legend(loc="best")Loading...
fig, ax = plt.subplots(layout="constrained")
(ln,) = ax.plot(
[],
[],
color="red",
label="Exacta",
linestyle="dashed",
linewidth=0.5,
)
ax.spines["bottom"].set_color("none")
ax.spines["top"].set_color("none")
ax.spines["left"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["left"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["left"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.spines["right"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["right"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["right"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.set_xlabel(xlabel=r"$x$")
ax.set_xlim(left=x[0], right=x[-1])
ax.set_ylim(bottom=U(x).min(), top=U(x).max())
ax.set_title(label=r"Solución exacta $u\left(x,t\right)=u(x-ct)$")
ax.legend(loc="best")
def init():
ln.set_data(x, U(x))
return (ln,)
def update(frame):
ln.set_data(x, U(x=x - c * (t[0] + frame * Δt)))
ax.set_ylabel(
ylabel=rf"$U\left(x, t={frame * Δt:.2f}\right)$", loc="top", rotation=0
)
return (ln,)
anim = FuncAnimation(
fig=fig,
func=update,
frames=tqdm(iterable=range(t.size), file=sys.stdout, colour="green"),
interval=1,
init_func=init,
blit=True,
).save(
filename="exactheaviside.gif",
writer=FFMpegWriter(
fps=90,
codec="libx265",
metadata={
"subject": "Numerical Analysis",
"title": "Exact solution",
"author": "Gloria Almozara Sainz",
"genre": "Mathematics",
"copyright": "2025",
"srcform": "Matplotlib 3.9.3",
"comment": "Numerical Simulation for advection PDE",
},
),
dpi=300,
savefig_kwargs={"transparent": True, "facecolor": "none"},
)
plt.close()Loading...
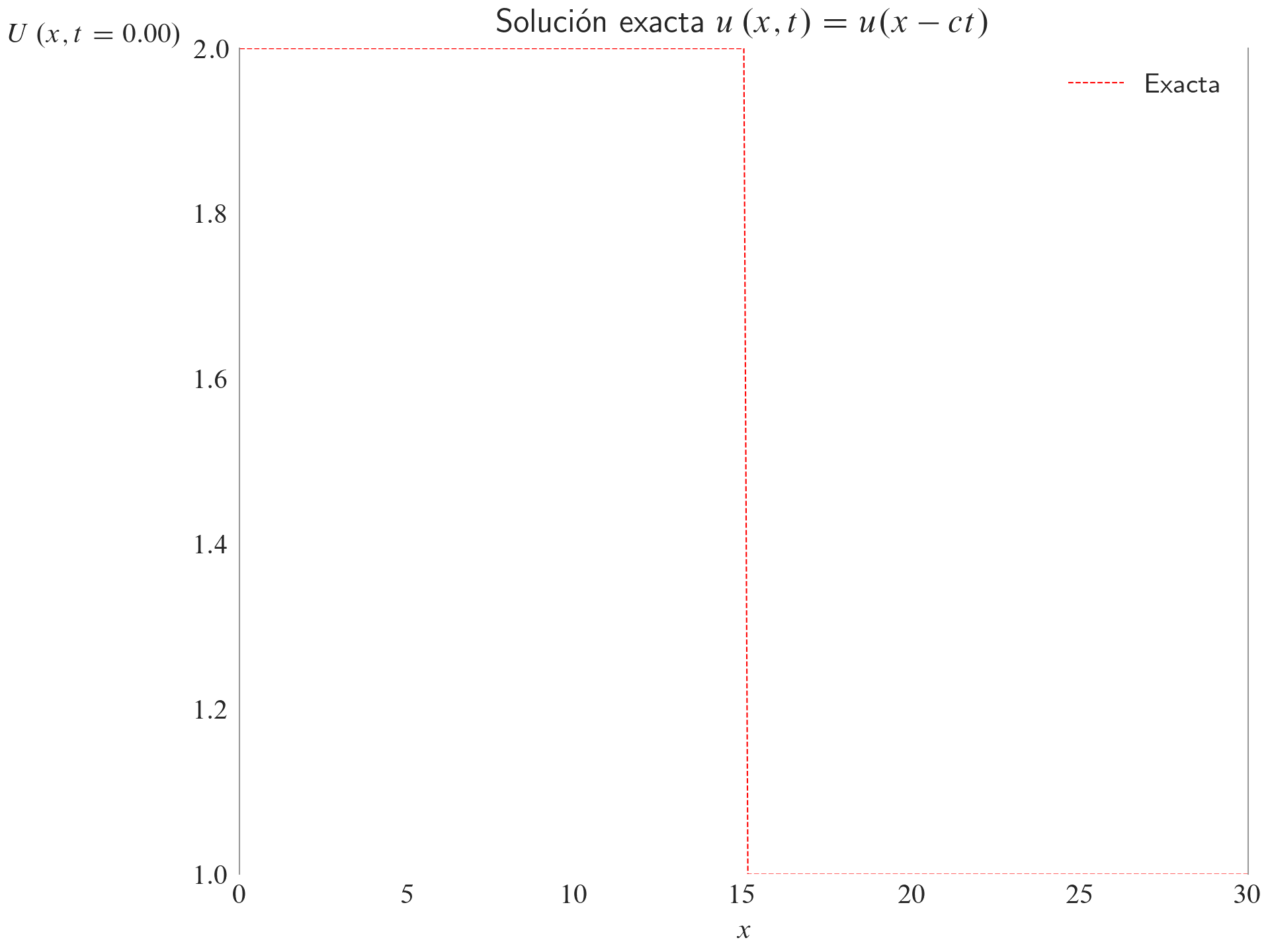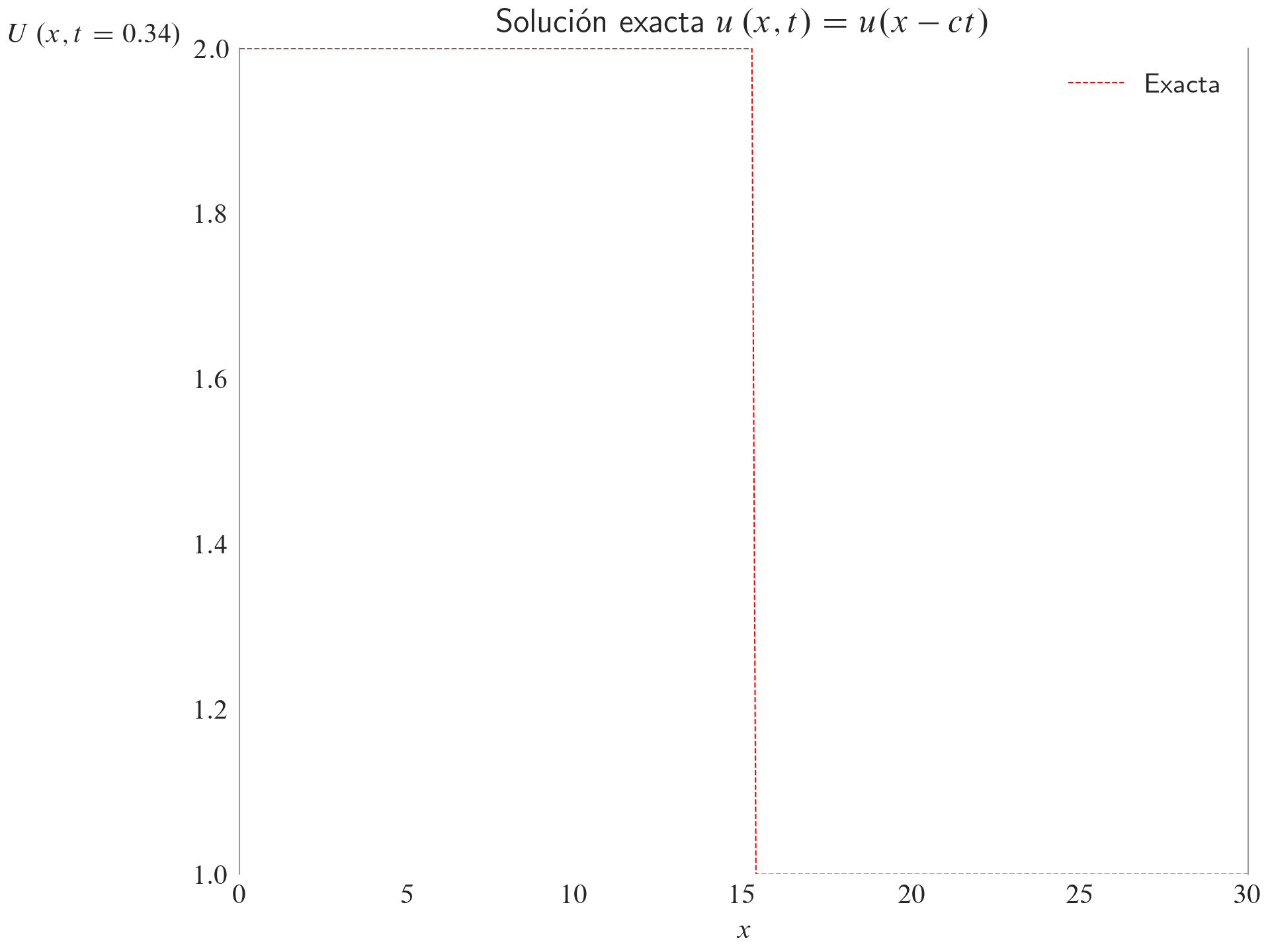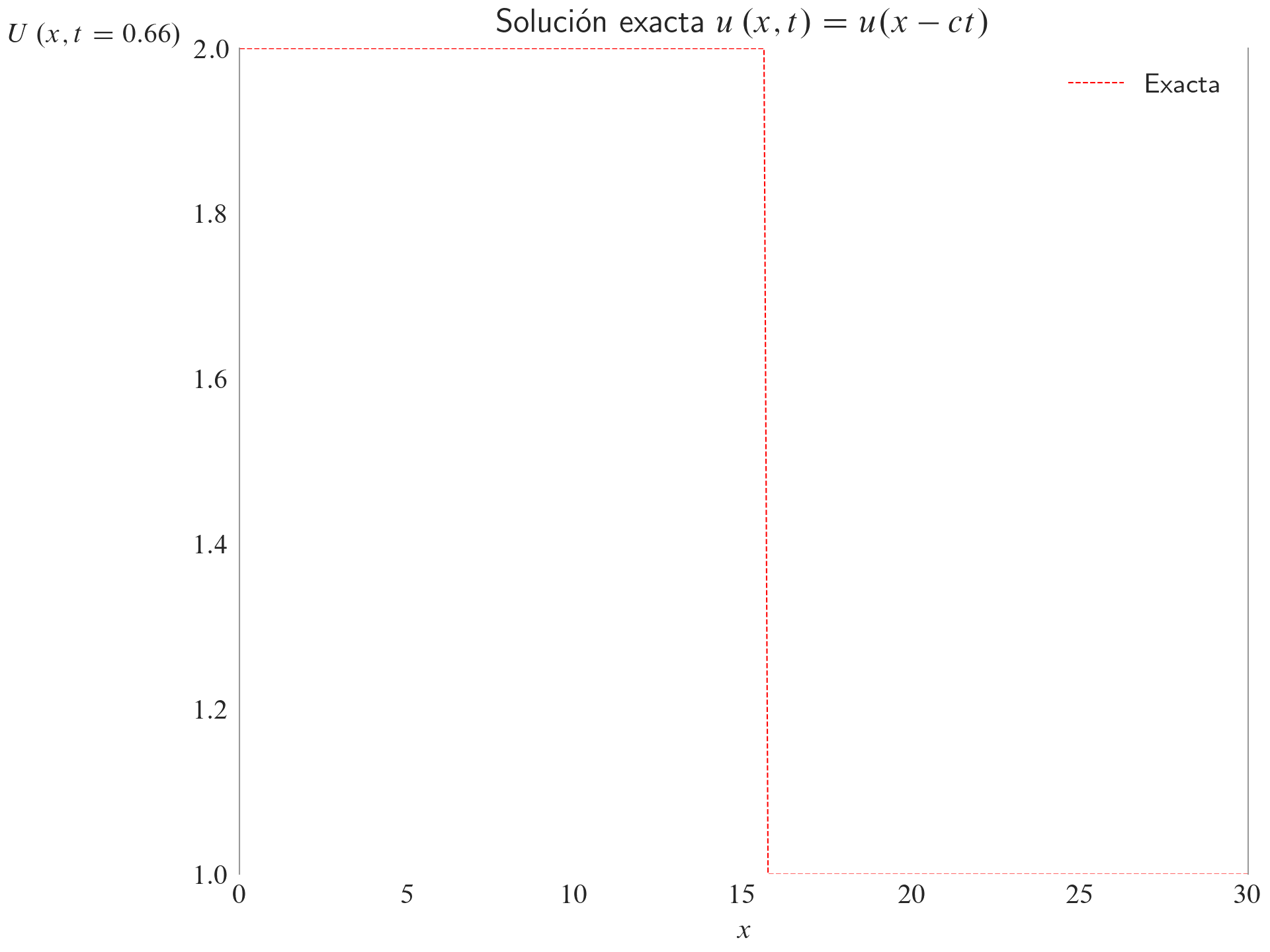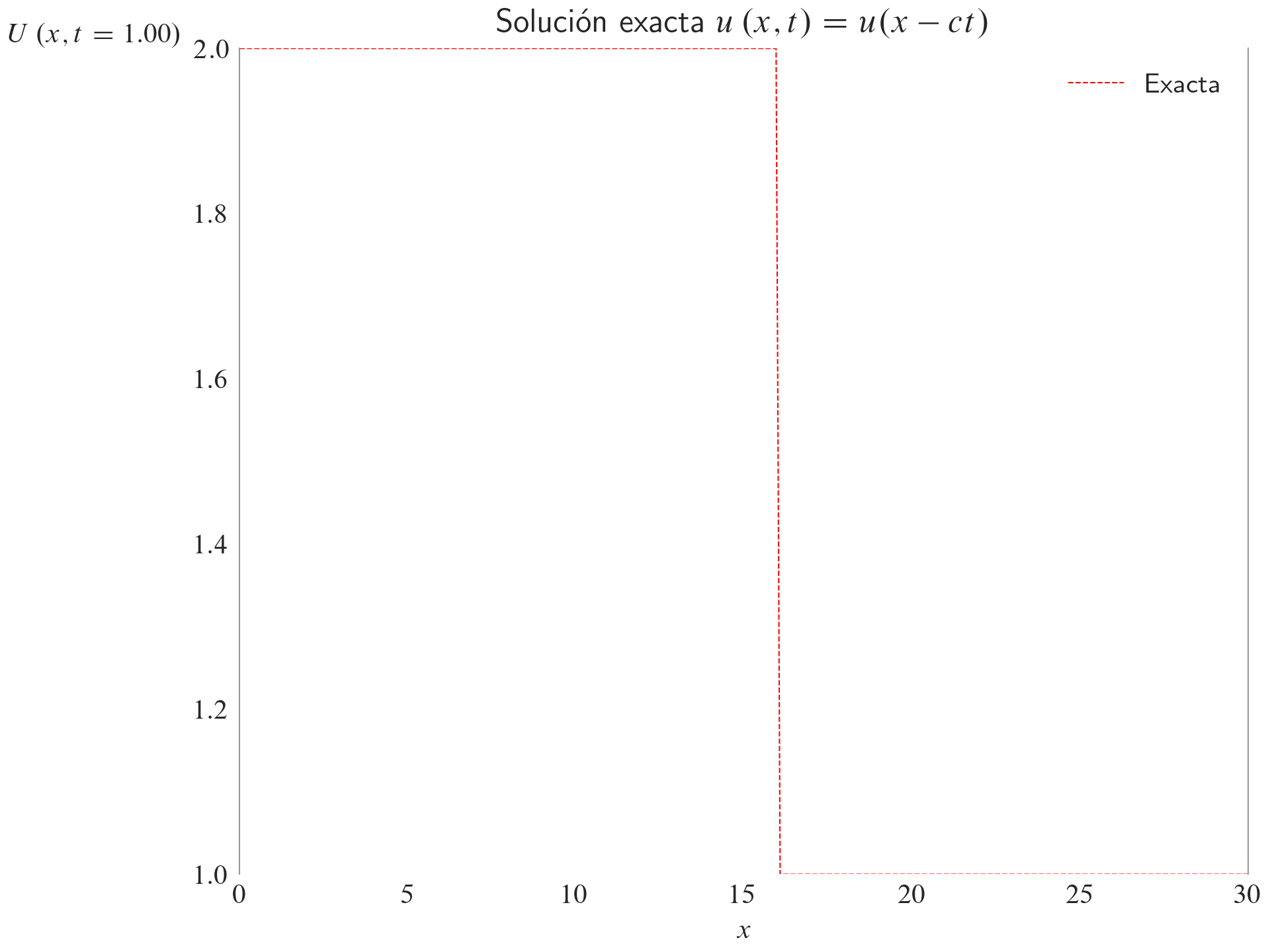
fig, ax = plt.subplots(layout="constrained")
(ln,) = ax.plot(
[],
[],
color="DarkBlue",
label="Exacta",
linestyle="dashed",
linewidth=0.5,
)
ln1 = ax.scatter(
x=[],
y=[],
c="blue",
label=rf"CFL $={cfl:.1f}$, $\Delta x={Δx:.3f}$",
s=0.4,
)
ax.spines["bottom"].set_color("none")
ax.spines["top"].set_color("none")
ax.spines["left"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["left"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["left"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.spines["right"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["right"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["right"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.set_xlabel(xlabel=r"$x$")
ax.set_xlim(left=x[0], right=x[-1])
ax.set_ylim(bottom=U(x).min(), top=U(x).max())
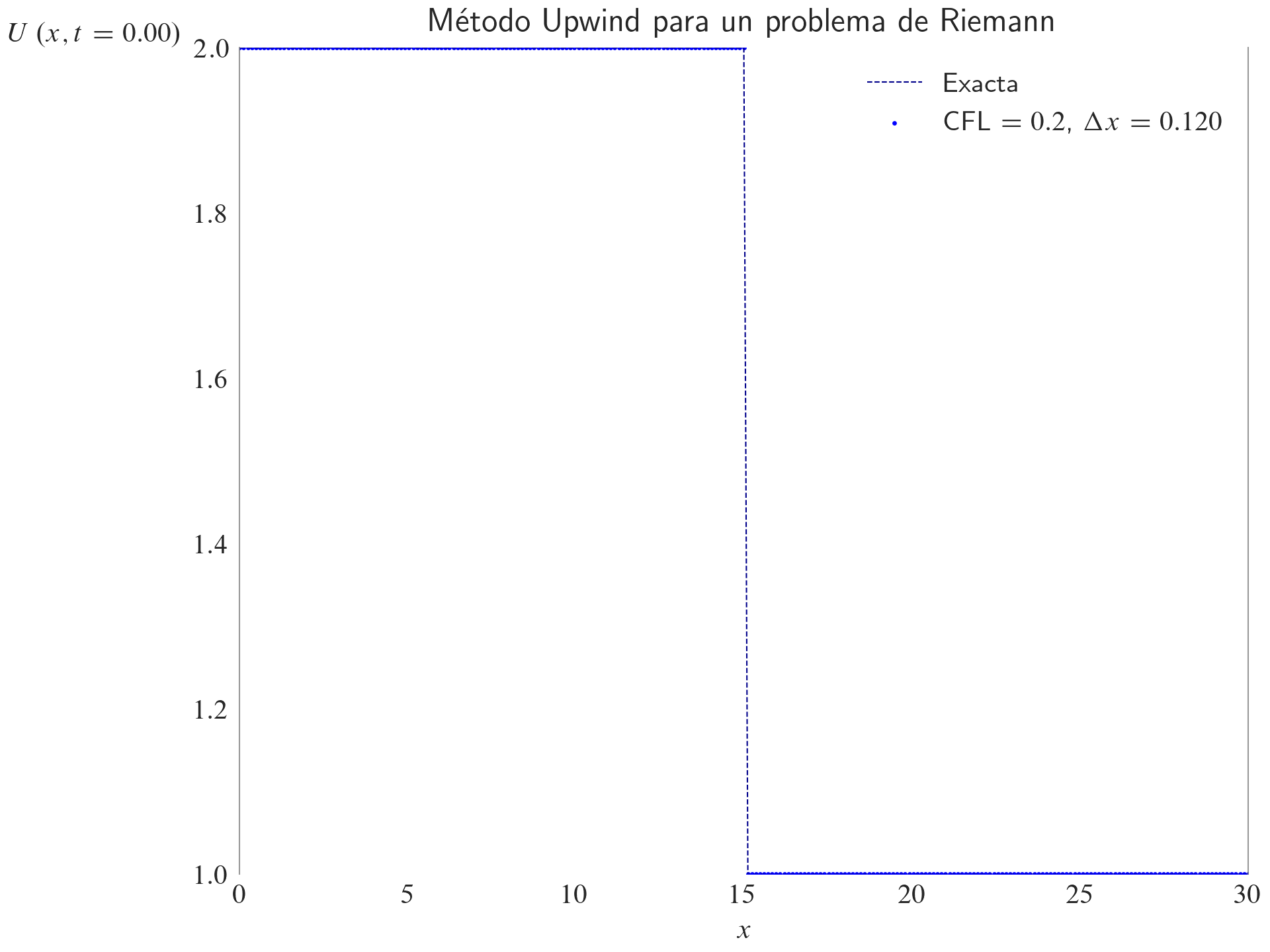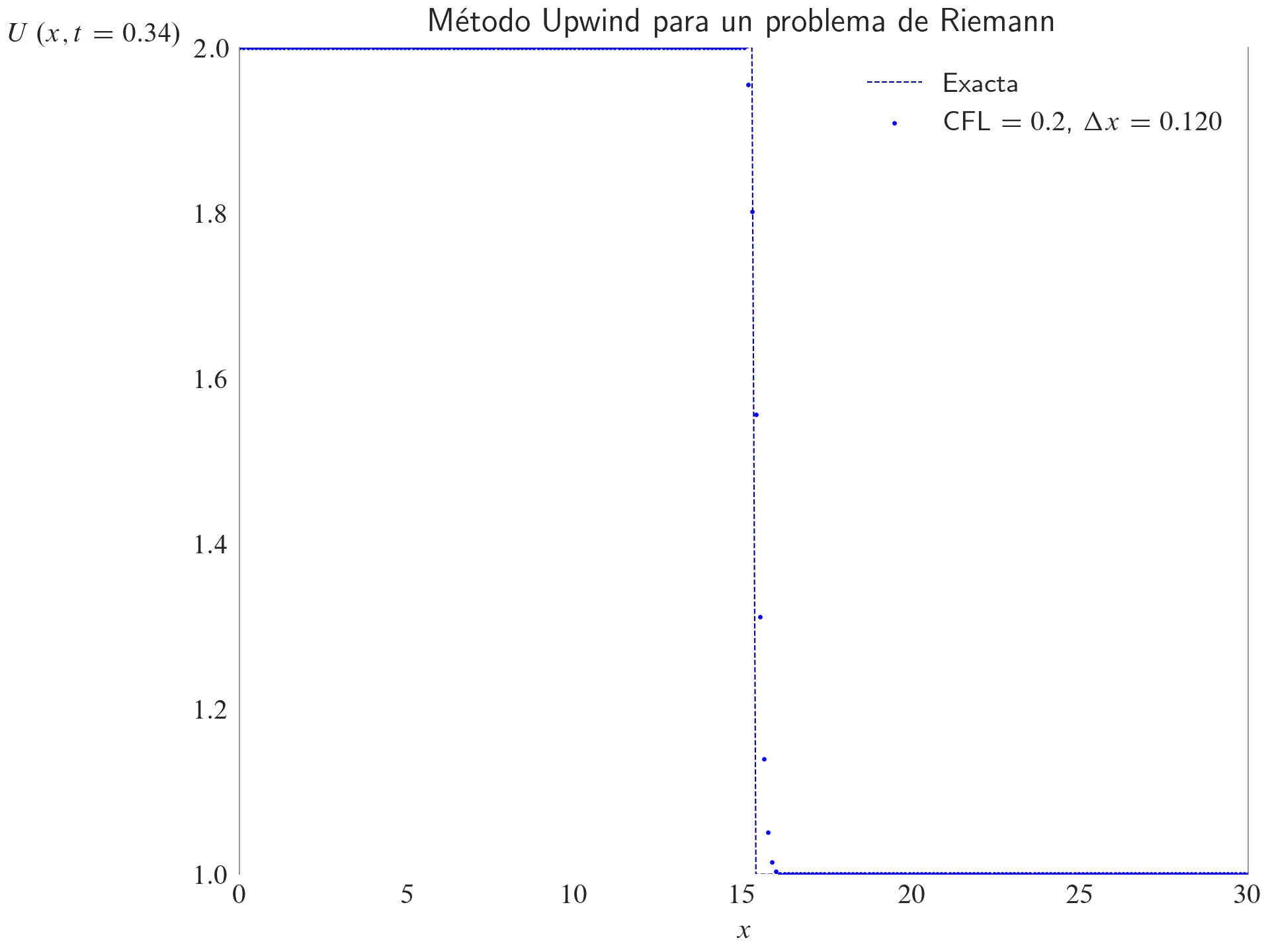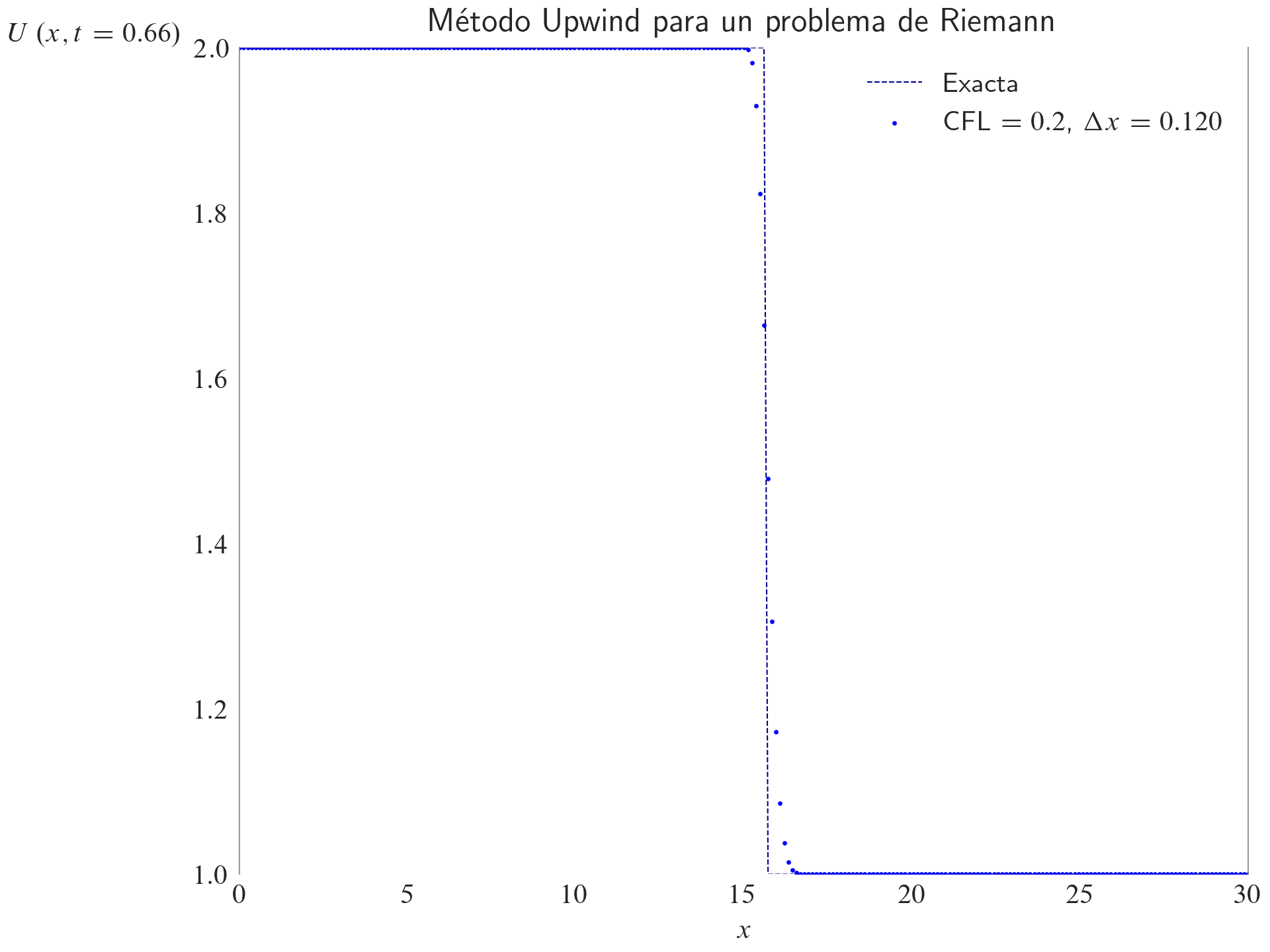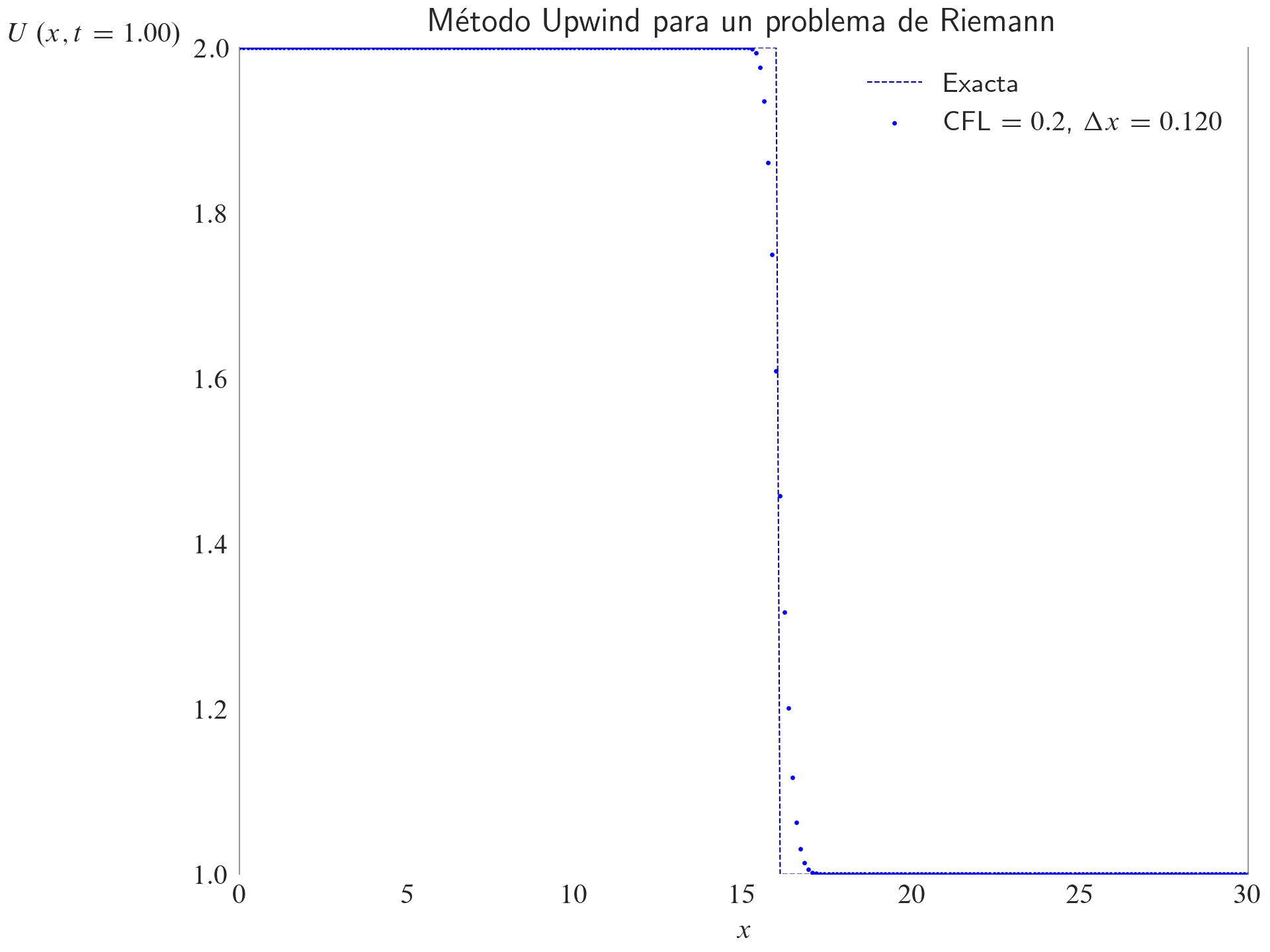
ax.set_title(label="Método Upwind para un problema de Riemann", loc="center")
ax.legend(loc="best")
U1 = U(x=x)
def init():
ln.set_data(x, U(x))
ln1.set_offsets(offsets=np.column_stack([x, U1]))
return (ln,)
def update(frame):
ln1.set_offsets(offsets=np.column_stack([x, U1]))
ln.set_data(x, U(x=x - c * frame * Δt))
U1[1:] -= cfl * (U1 - np.roll(U1, 1))[1:]
ax.set_ylabel(
ylabel=rf"$U\left(x, t={frame * Δt:.2f}\right)$", loc="top", rotation=0
)
return (ln,)
anim = FuncAnimation(
fig=fig,
func=update,
frames=tqdm(iterable=range(t.size), file=sys.stdout, colour="green"),
interval=1,
init_func=init,
blit=True,
).save(
filename="upwindheaviside.gif",
writer=FFMpegWriter(
fps=90,
codec="libx265",
metadata={
"subject": "Numerical Analysis",
"title": "Exact solution",
"author": "Gloria Almozara Sainz",
"genre": "Mathematics",
"copyright": "2025",
"srcform": "Matplotlib 3.9.3",
"comment": "Numerical Simulation for advection PDE",
},
),
dpi=300,
savefig_kwargs={"transparent": True, "facecolor": "none"},
)
plt.close()Loading...
fig, ax = plt.subplots(layout="constrained")
(ln,) = ax.plot(
[],
[],
color="DarkBlue",
label="Exacta",
linestyle="dashed",
linewidth=0.5,
)
ln1 = ax.scatter(
x=[],
y=[],
c="blue",
label=rf"CFL $={cfl:.1f}$, $\Delta x={Δx:.3f}$",
s=0.4,
)
ax.spines["bottom"].set_color("none")
ax.spines["top"].set_color("none")
ax.spines["left"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["left"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["left"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.spines["right"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["right"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["right"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.set_xlabel(xlabel=r"$x$")
ax.set_xlim(left=x[0], right=x[-1])
ax.set_ylim(bottom=U(x).min(), top=U(x).max())
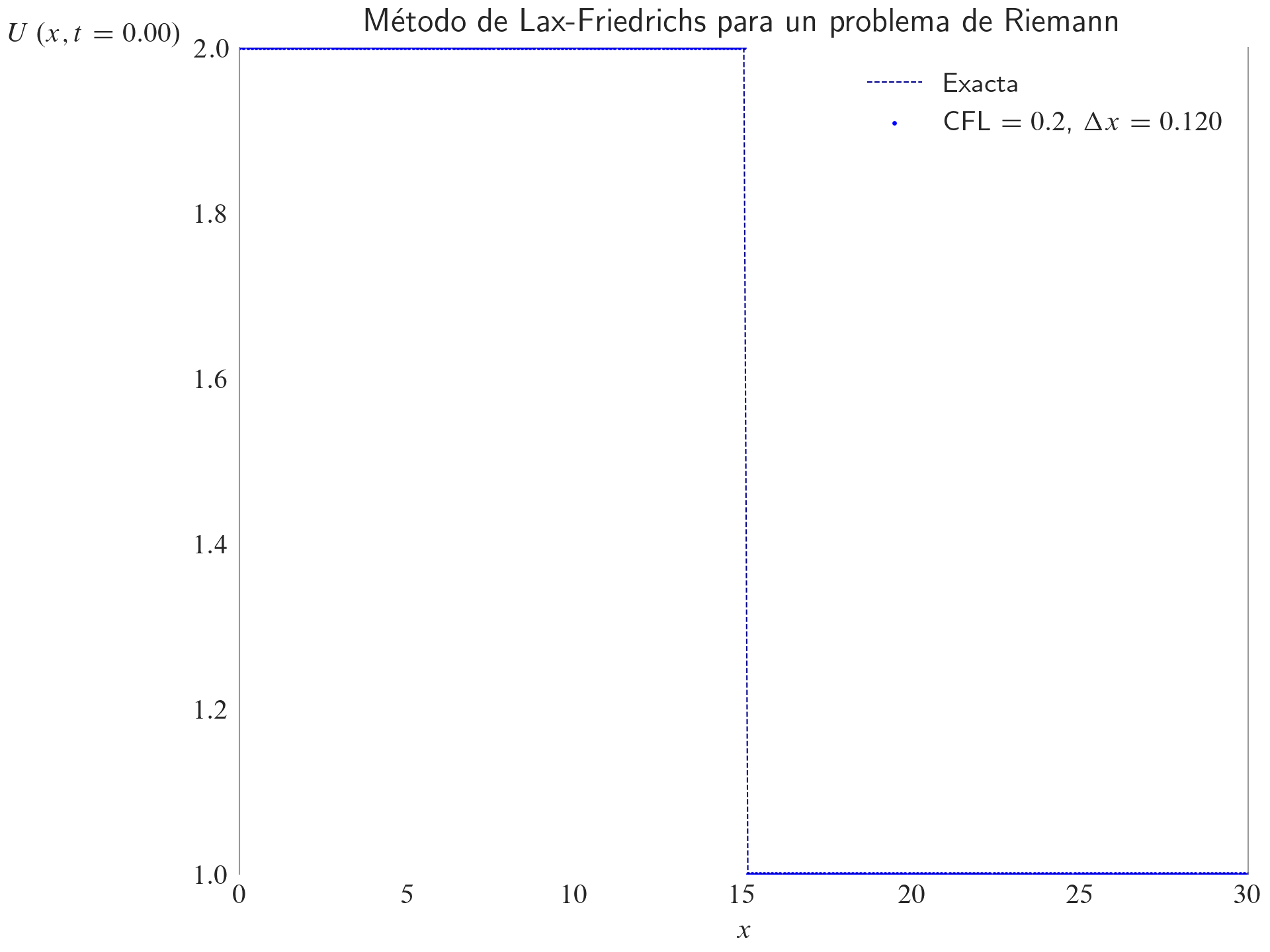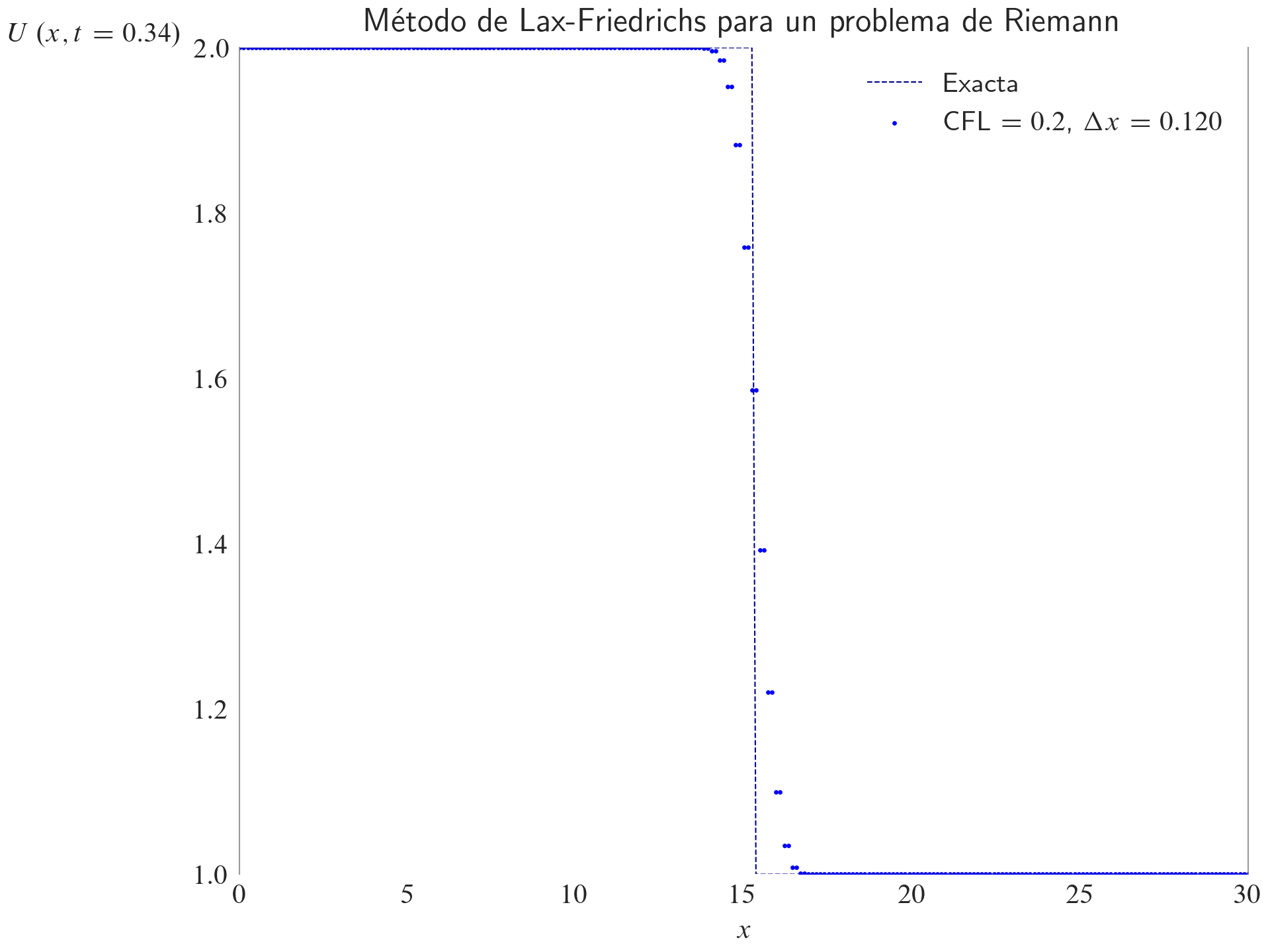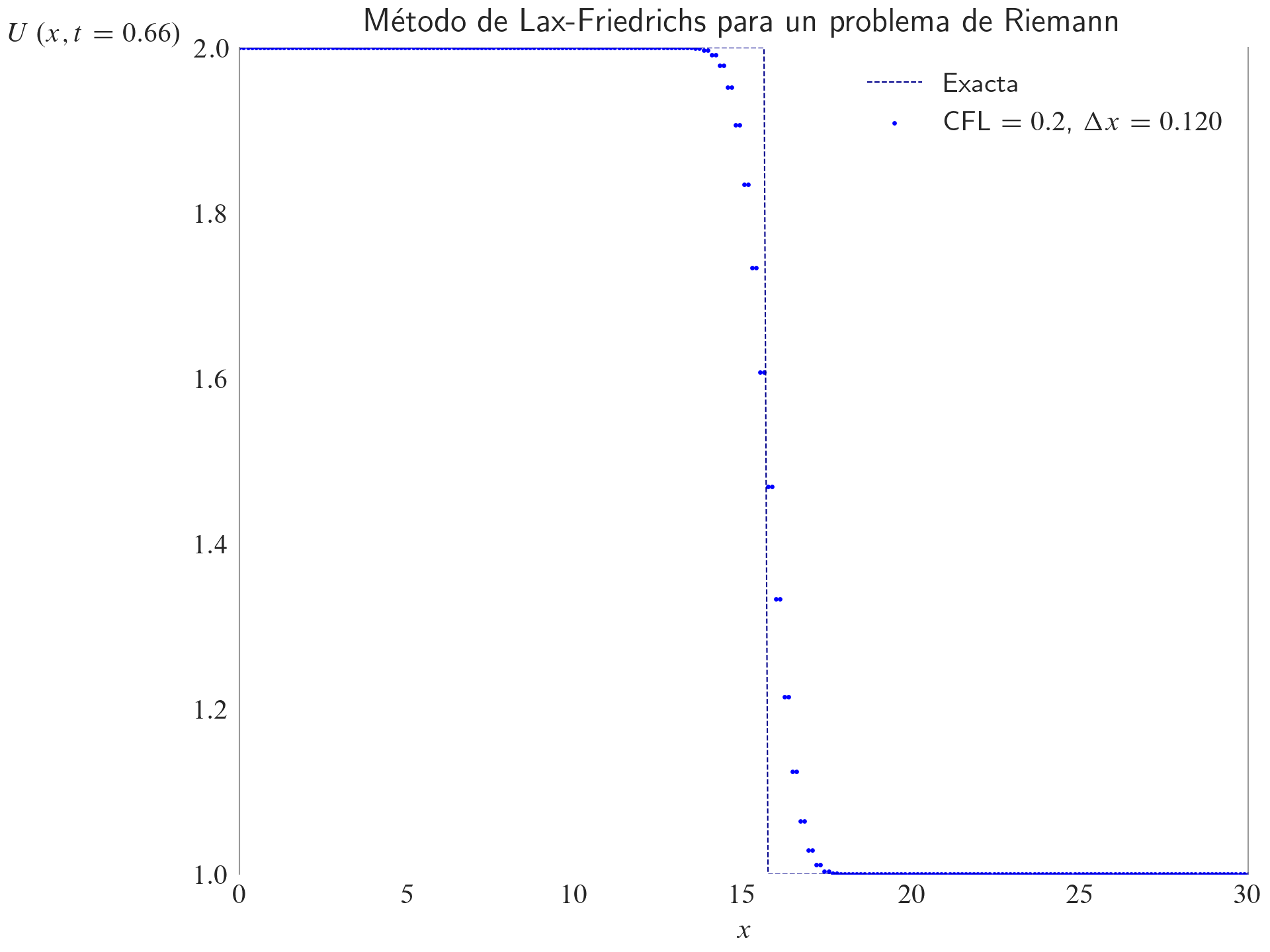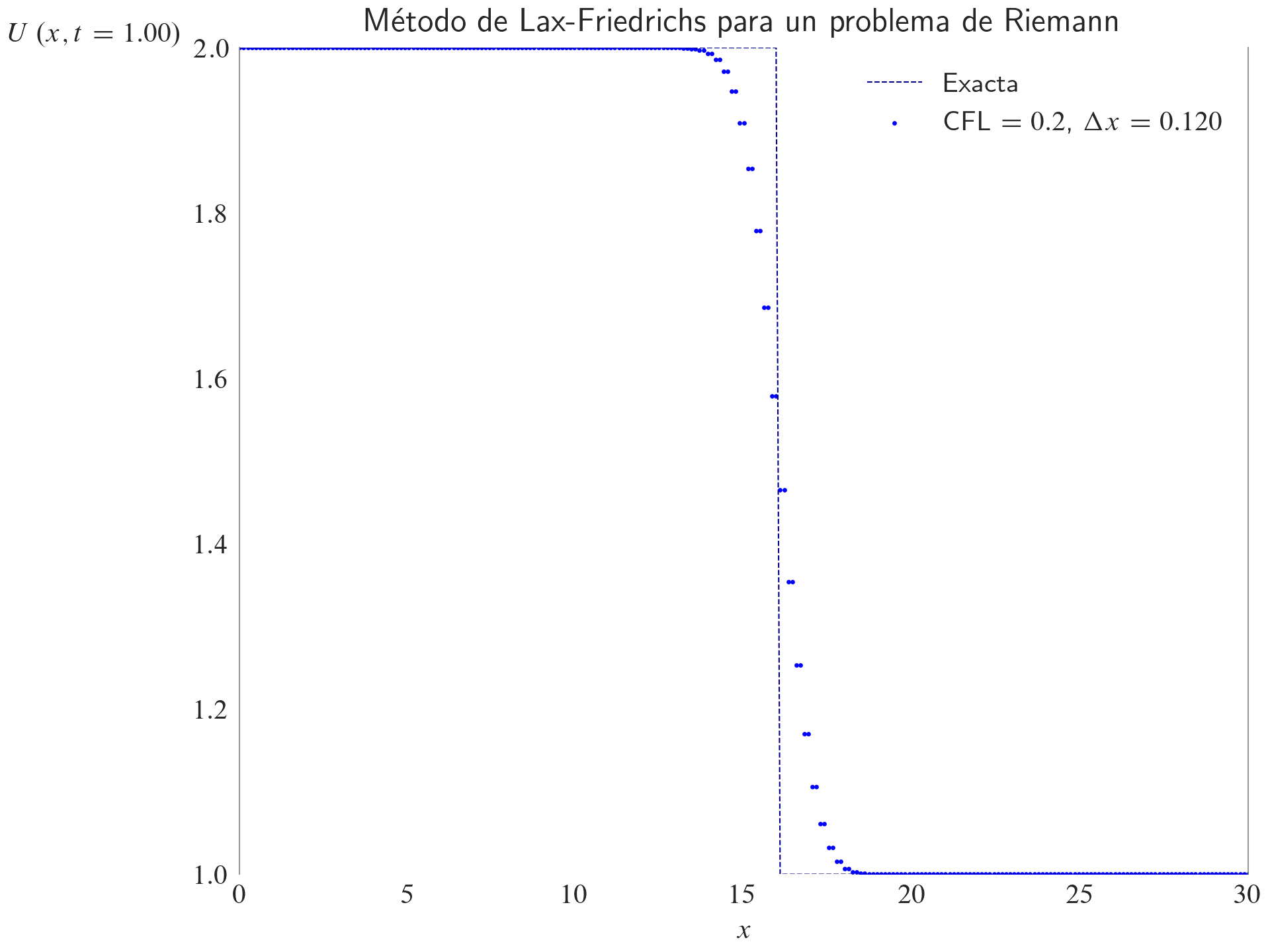
ax.set_title(label="Método de Lax-Friedrichs para un problema de Riemann", loc="center")
ax.legend(loc="best")
U1 = U(x=x)
def init():
ln.set_data(x, U(x))
ln1.set_offsets(offsets=np.column_stack([x, U1]))
return (ln,)
def update(frame):
ln1.set_offsets(offsets=np.column_stack([x, U1]))
ln.set_data(x, U(x=x - c * frame * Δt))
U1[1:-1] = (
0.5 * (np.roll(U1, -1) + np.roll(U1, 1))[1:-1]
- 0.5 * cfl * (np.roll(U1, -1) - np.roll(U1, 1))[1:-1]
)
ax.set_ylabel(
ylabel=rf"$U\left(x, t={frame * Δt:.2f}\right)$", loc="top", rotation=0
)
return (ln,)
anim = FuncAnimation(
fig=fig,
func=update,
frames=tqdm(iterable=range(t.size), file=sys.stdout, colour="green"),
interval=1,
init_func=init,
blit=True,
).save(
filename="lax-friedrichsheaviside.gif",
writer=FFMpegWriter(
fps=90,
codec="libx265",
metadata={
"subject": "Numerical Analysis",
"title": "Exact solution",
"author": "Gloria Almozara Sainz",
"genre": "Mathematics",
"copyright": "2025",
"srcform": "Matplotlib 3.9.3",
"comment": "Numerical Simulation for advection PDE",
},
),
dpi=300,
savefig_kwargs={"transparent": True, "facecolor": "none"},
)
plt.close()Loading...
fig, ax = plt.subplots(layout="constrained")
(ln,) = ax.plot(
[],
[],
color="DarkBlue",
label="Exacta",
linestyle="dashed",
linewidth=0.5,
)
ln1 = ax.scatter(
x=[],
y=[],
c="blue",
label=rf"CFL $={cfl:.1f}$, $\Delta x={Δx:.3f}$",
s=0.4,
)
ax.spines["bottom"].set_color("none")
ax.spines["top"].set_color("none")
ax.spines["left"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["left"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["left"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.spines["right"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["right"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["right"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.set_xlabel(xlabel=r"$x$")
ax.set_xlim(left=x[0], right=x[-1])
ax.set_ylim(bottom=U(x).min() - 0.01, top=U(x).max() + 0.01)
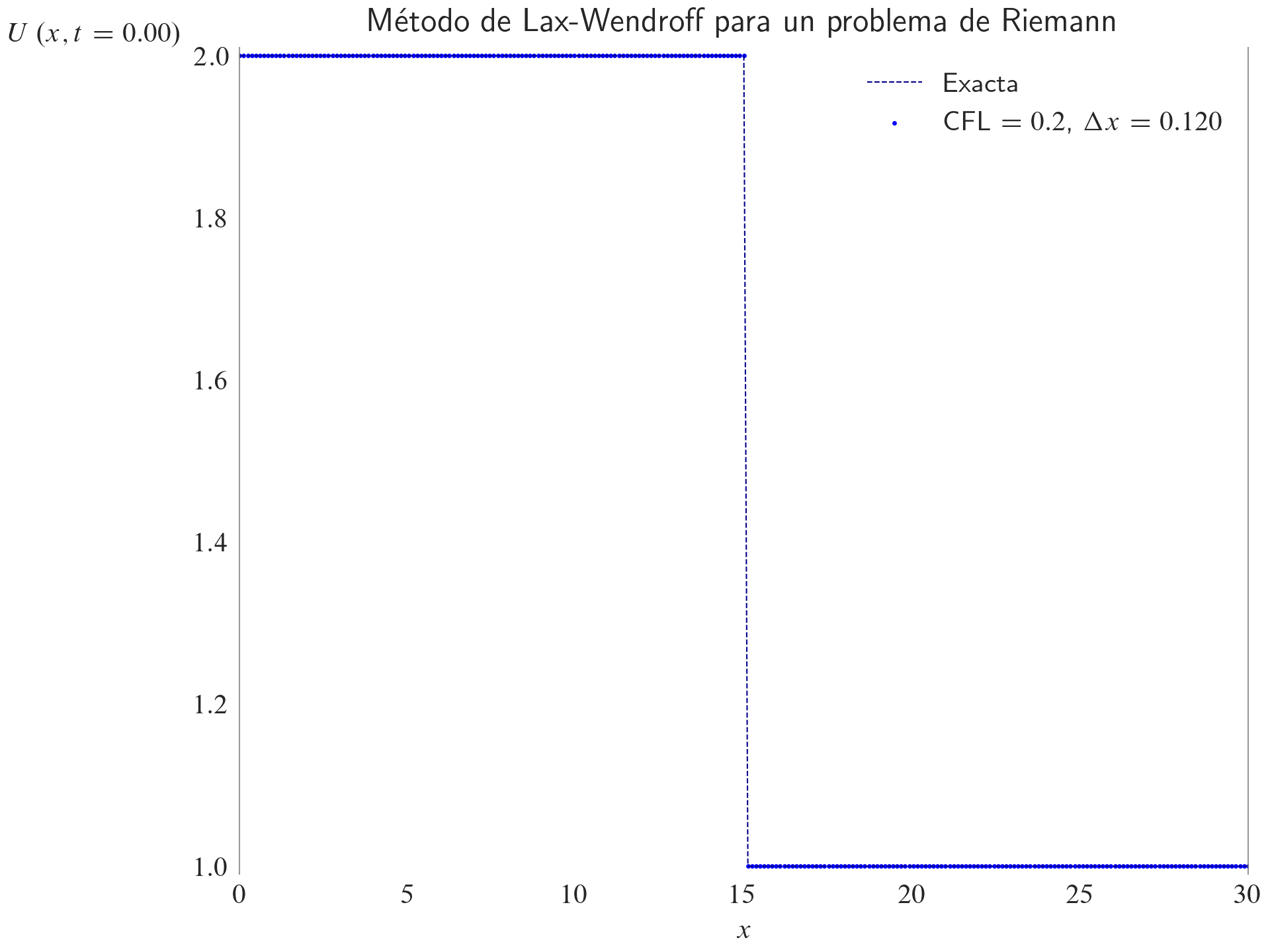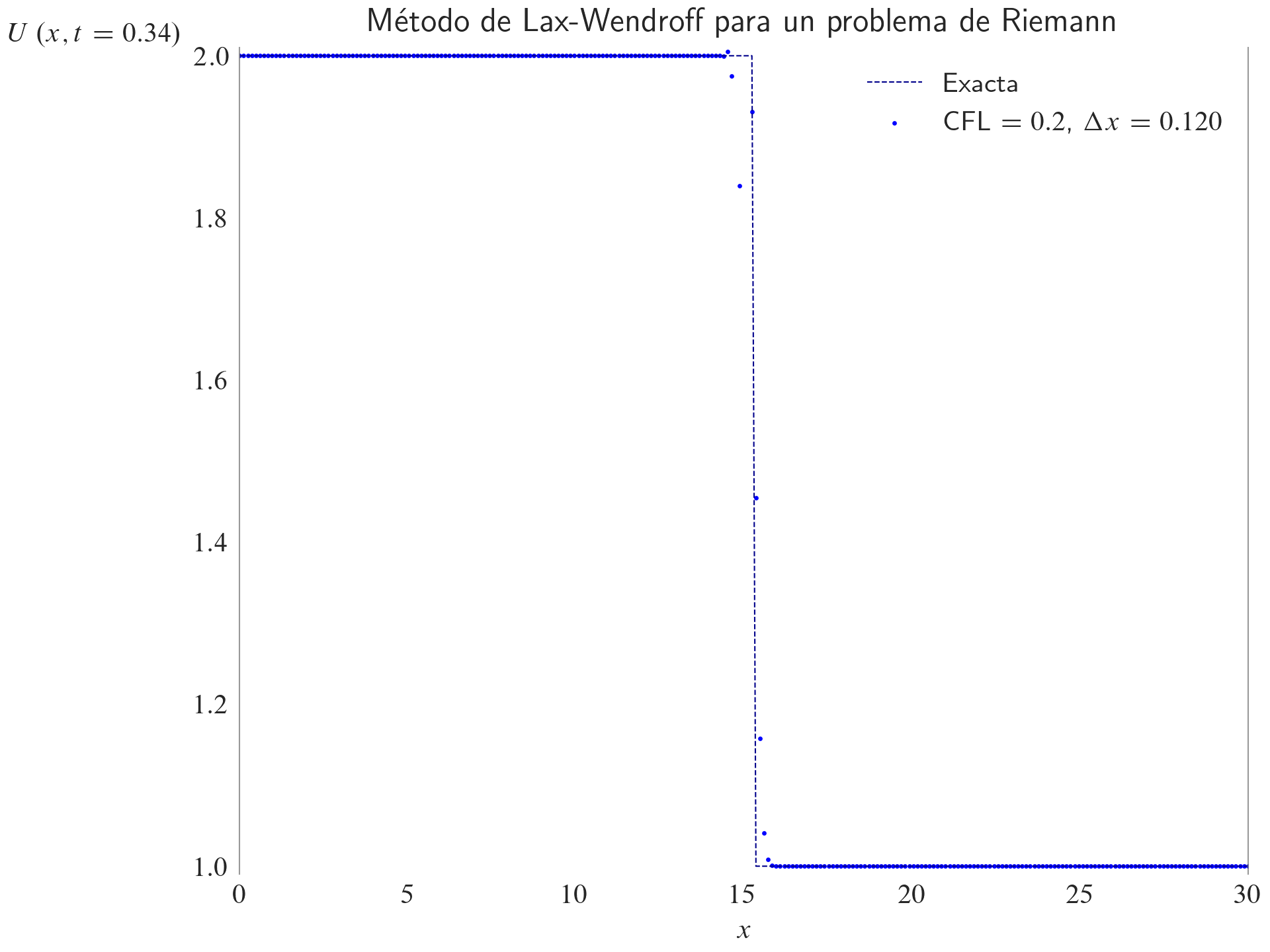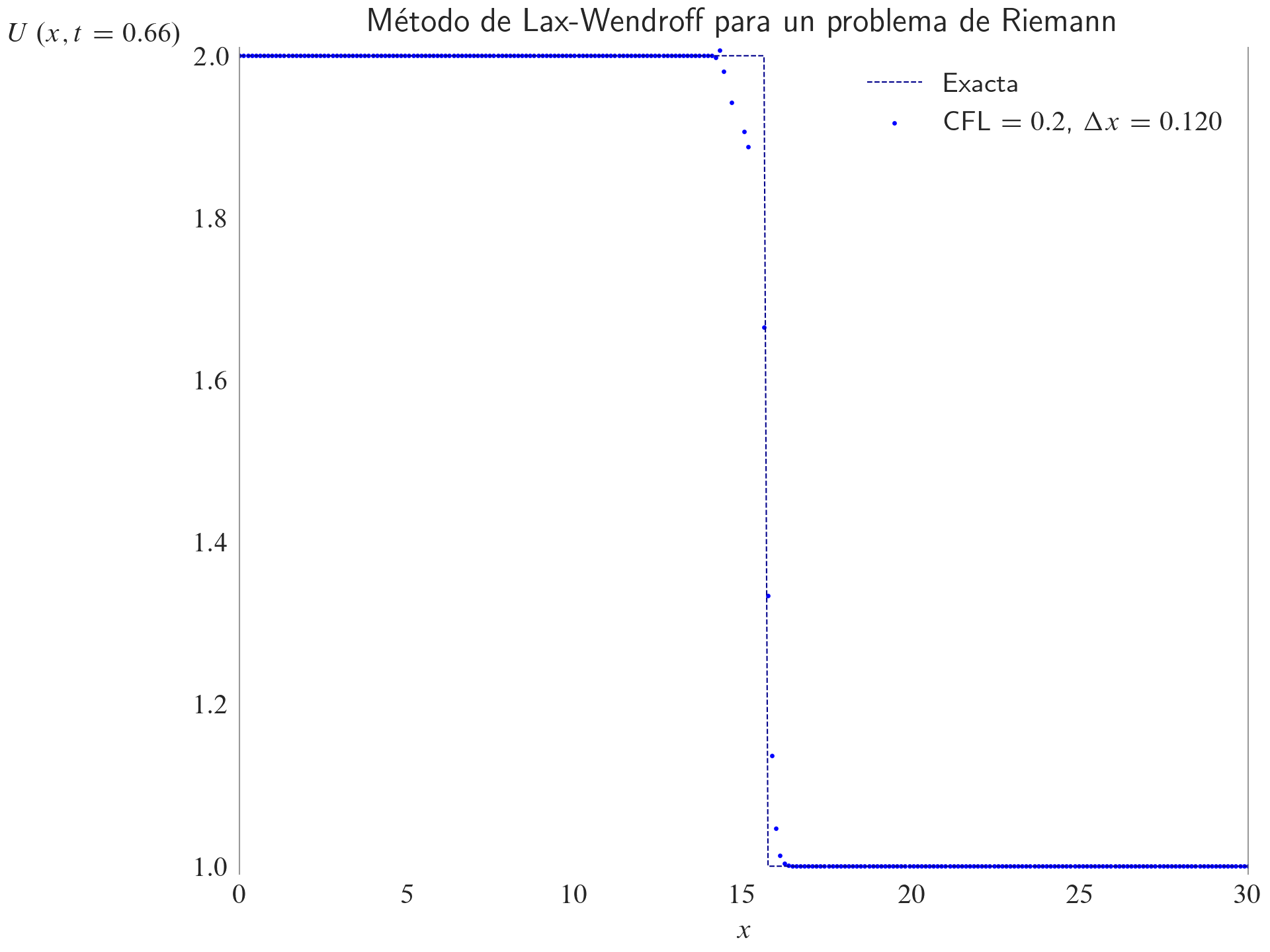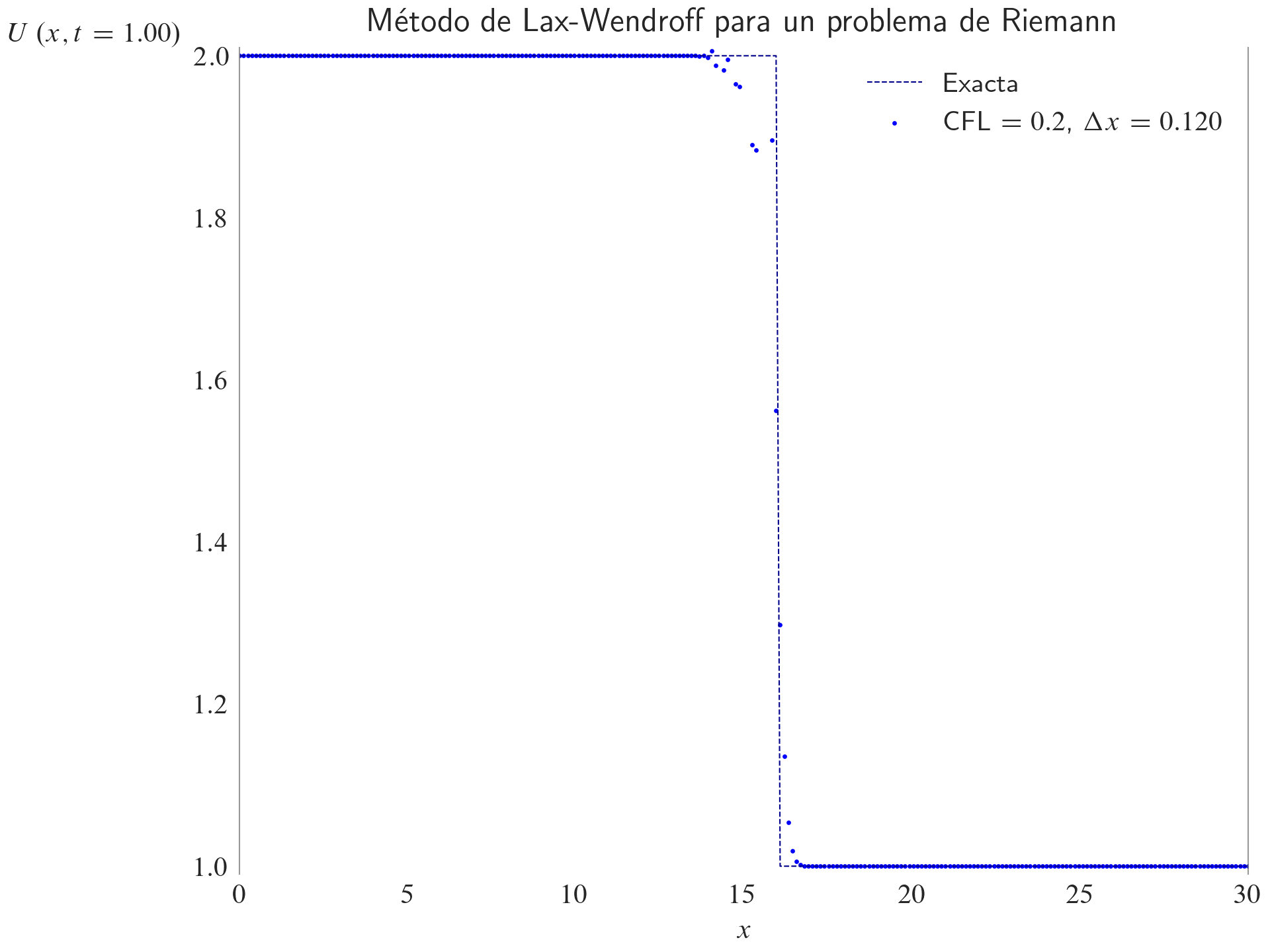
ax.set_title(label="Método de Lax-Wendroff para un problema de Riemann", loc="center")
ax.legend(loc="best")
U1 = U(x=x)
def init():
ln.set_data(x, U(x))
ln1.set_offsets(offsets=np.column_stack([x, U1]))
return (ln,)
def update(frame):
ln1.set_offsets(offsets=np.column_stack([x, U1]))
ln.set_data(x, U(x=x - c * frame * Δt))
U1[1:-1] -= (
0.5 * cfl * (np.roll(U1, -1) - np.roll(U1, 1))[1:-1]
- 0.5 * cfl**2 * (np.roll(U1, -1) - 2 * U1 + np.roll(U1, 1))[1:-1]
)
ax.set_ylabel(
ylabel=rf"$U\left(x, t={frame * Δt:.2f}\right)$", loc="top", rotation=0
)
return (ln,)
anim = FuncAnimation(
fig=fig,
func=update,
frames=tqdm(iterable=range(t.size), file=sys.stdout, colour="green"),
interval=1,
init_func=init,
blit=True,
).save(
filename="lax-wendroffheaviside.gif",
writer=FFMpegWriter(
fps=90,
codec="libx265",
metadata={
"subject": "Numerical Analysis",
"title": "Exact solution",
"author": "Gloria Almozara Sainz",
"genre": "Mathematics",
"copyright": "2025",
"srcform": "Matplotlib 3.9.3",
"comment": "Numerical Simulation for advection PDE",
},
),
dpi=300,
savefig_kwargs={"transparent": True, "facecolor": "none"},
)
plt.close()Loading...
x, Δx = np.linspace(start=0, stop=1, num=41, retstep=True)
t, Δt = np.linspace(start=0, stop=0.15, num=301, retstep=True)def U(x):
return np.exp(-np.power(x - 15, 2))def V(x):
return np.exp(-np.power(x - 15, 2)) + 2fig, ax = plt.subplots(layout="constrained")
ax.plot(
x,
U(x),
color="red",
label=r"$U_{0}\left(x\right)$",
linestyle="solid",
linewidth=1.0,
)
ax.plot(
x,
V(x),
color="red",
label=r"$V_{0}\left(x\right)$",
linestyle="solid",
linewidth=1.0,
)
ax.spines["bottom"].set_color("none")
ax.spines["top"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["top"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["top"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.spines["left"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["left"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["left"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
ax.spines["right"].set_alpha(alpha=0.8)
ax.spines["right"].set_edgecolor(color="gray")
ax.spines["right"].set_linewidth(w=0.5)
# ax.set_xlim(left=x[0], right=x[-1])
# ax.set_ylim(bottom=0, top=1)
ax.set_title(
label=r"Condición inicial $U_{0}\left(x\right)=e^{-{\left(x-15\right)}^{2}}$",
loc="center",
)
ax.legend(loc="best")Loading...